Controlled oral word association task
From Psy3241
Controlled Oral Word Association Task (COWAT):
COWAT Overview:
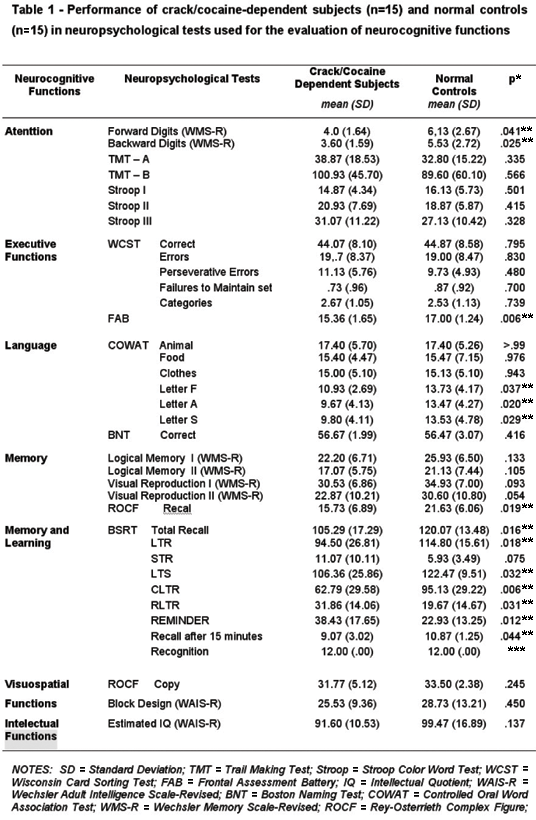
The COWAT (Benton, 1967) is a cognitive test of verbal processing ability used to assess brain impairment. Verbal processing ability and verbal fluency are considered executive functions. The emphasis on these tests focuses on the degree of discrepancy (as opposed to consistency) between current functioning and an estimated pre-impairment functioning. The COWAT assesses the subject’s ability to spontaneously produce words that begin with specific letters within a certain time limit. In particular, the test uses the letters F, A, and S. Before the test begins, the patient is given a practice trial with a different letter. Other letters may be added to the tests for comparison.
COWAT’s Applications and Research:
The COWAT has been used to research the process of cognitive aging in accordance with the Frontal Aging Hypothesis (Dempster, 1992). This theory is based on the assumption that deterioration of the frontal lobes during the normal aging process leads to cognitive impairment similar to patients who have lesions in their frontal lobes. Since the frontal lobes are involved in executive functioning, the COWAT has been used as one measure of this functioning in the elderly. Research has shown that one should take caution when administering the COWAT to evaluate older people’s level of executive functioning for the Frontal Aging Hypothesis. This caution is due to arguments that executive functioning might not be one single mechanism; rather, it is possible that there are independent executive abilities. As a result, the COWAT alone as an assessment of executive functioning may not be an accurate representation of executive decline.
The COWAT has been used in searches for differential diagnoses for dementia. The COWAT has been used to collect normative data from a range of subjects to establish norms for age, gender, education level, etc. Normative data allows for comparison with other neuropsychological tests that evaluate word knowledge and speed of verbal processing to examine the interrelationship between the instruments. Other applications include measuring cognitive impairment due to Wilson’s Disease, HIV, drug addiction.
Sources:
http://usq.edu.au/users/senior/Posters/JCordellPoster.htm
Rodrigues-Aranda, C., & Sundet, K. (2006) The Frontal Hypothesis of Cognitive Aging: Factor structure and age effects on four frontal tests among healthy individuals. The Journal of Genetic Psychology, 167(3), 269-288.