Special Physical Diagnosis - Newborn
From Iusmicm
[edit] Newborn Physical Exam
[edit] General
- There are 3 questions we are trying to answer in the newborn exam:
- How well is the newborn transitioning to extrauterine life?
- Is there any evidence of birth trauma?
- Is there any evidence of congenital malformation?
- We examine 5 signs immediately after birth to assess cardio-pulmonary function:
- Color
- Heart rate
- Reflex irritability
- Muscle tone
- Respiratory effort
- The Apgar scale (after Virginia Apgar) is a measure of cardiopulmonary function.
- Higher is better
- Each of the 5 aforementioned gets a score of 0, 1, or 2.
- For example, a blue or pale newborn gets a "color" Apgar score of 0 while a pink newborn gets a score of 2.
- Add up the score for each category (color, heart rate, reflex irritability, muscle tone, and respiratory effort) to get the total Apgar score.
- A score of 3-4 means the baby needs to be resuscitated.
[edit] General Assessment
- We care about true gestational age because it is a good predictor of the struggles the newborn will face in transitioning to extrauterine life.
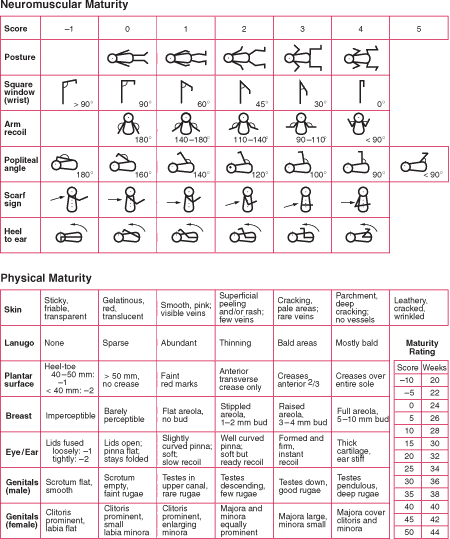
- We assess true gestational age by a subjective clinical observation and also by a 21 point objective observation (Dubowitz Clinical Assessment).
- Dubowitz contains 10 neurological signs and 11 external signs.
- Like Apgar, the total scores are summed and the higher the score the more fully developed the newborn (score of 37-41 is norm for full term baby).
- NB: "term infant" (37-41 or 38-42 weeks), "preterm" (<37 weeks), "post-term" (> 42 weeks)
- The newborn is weighed and the weight is controlled by gestational age and classified into "small for gestational age (SGA)" (<10th percentile), "appropriate for gestational age (AGA)" (10th-90th percentile), or "large for gestational age (LGA)".
...