Dermatology - Introduction
From Iusmicm
Contents |
[edit] Motivation
- The skin is the biggest, thus most important organ
- Skin diseases account for 17% of all primary care visits
[edit] Objectives
- Basic principles
- Introduction to dermatologists
- Common skin problems
- Complexity of dermatologic disorders
[edit] Expectations
- Structure and function of the skin
- History and physical examination (learn the vocab)
- Recognize the clinical (and histologic) hallmarks of diseases discussed
- Know how and when to refer a patient
[edit] Structure and Function
- Three parts: epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous.
- Epidermis:
- Has keratinocytes, melanocytes, and langerhans cells
- Dermis:
- Has fibroblasts and blood vessels
- Subcutaneous
[edit] Keratinocytes
- Makes up most of the epidermis.
- Keeps in what should be in and out what should be out
- Barrier Function: form the stratum corneum
- Produce cytokines and inflammatory molecules
- Produce antimicrobial proteins and lipids; more potent than anything we can prescribe
- Metabolize drugs
- Arm skin:

- Finger skin:
- Has different keratins than has the arm
[edit] Melanocytes
- Melanocytes determine how much melanin and therefore the pigmentation of the pt
- Produce pigment
- Pigment protects against ultraviolet radiation
- Vitiligo: loss of melanocytes through autoimmune destruction
[edit] Langerhans cells
- Macrophage-like cells in epidermis
- Important for antigen recognition
- About 1/3 of all T cells have been educated in the skin



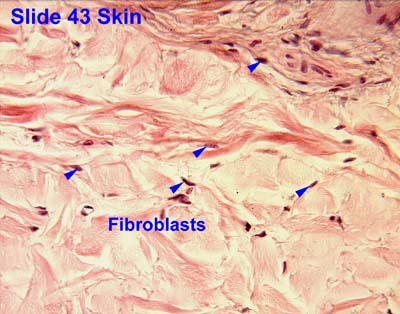
[edit] Fibroblasts
- Found in the dermis
- Produce collagen and ground substance
- Keloid scar is an example of excessive fibroblast activity





[edit] Vocabulary
- Important for proper communication of observations
- Primary versus Secondary lesions
- Primary lesion: basic lesion that defines a disease process
- Secondary lesion: lesions that evolve during the skin disease process or are created by scratching or infection
[edit] Primary lesions
- Basic lesions that defines a disease process
[edit] Macule / Patch
- Macule: Circumcised, flat (non-palpable), discolored (hence you can see it)
- Discoloration: brown, blue, red, hypopigmented
- A tattoo is an artificial papule
- Large macules (~> 2cm) are called "patches"
- Port-wine stain is an example of a macule




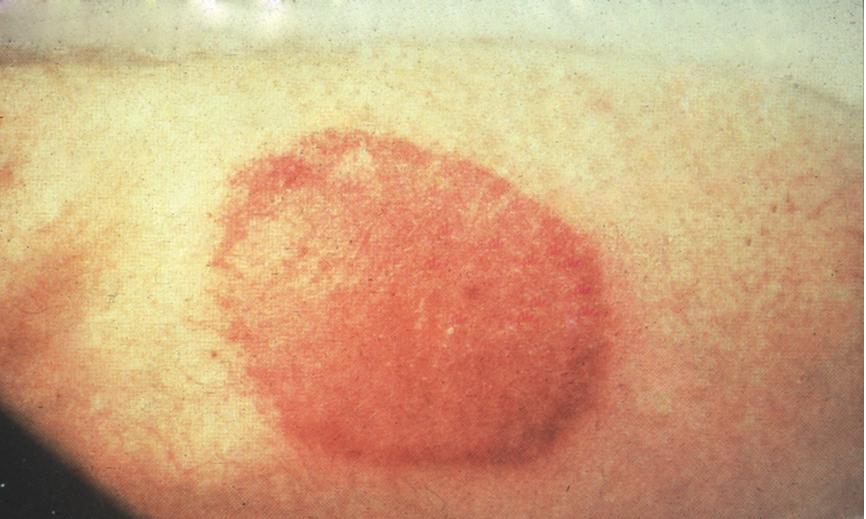
[edit] Papule / Plaque
- Elevated, solid, 0.5-1 cm diameter
- Larger is a plaque
- Confluent papules are called "plaques"
- Can vary in color
- Note that if it is circumscribed it is a nodule
- Papules:
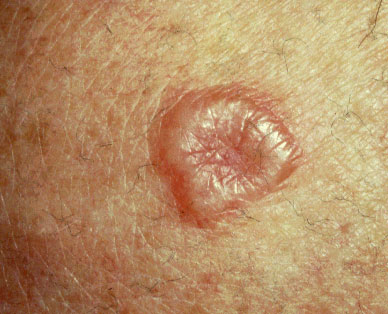
[edit] Nodule / Tumor
- Circumscribed, elevated, solid, 0.5-1 cm diameter
- Larger is a tumor
- Nodule:
- Tumor:
[edit] Wheal
- Firm, edematous plaque resulting because of infiltration of the dermis with fluid
- Example is urticaria (hives) or a TB test
- Wheals are transient, may only last hours



- http://itsmysocalledlife.files.wordpress.com/2009/02/190px-urtikaria_fuss.jpg%3Fw%3D190%26h%3D143
[edit] Pustule
- Circumscribed collection of leukocytes and free fluid, varies in size








[edit] Vesicle / Bulla
- Circumscribed collection of free fluid up to 0.5 cm diameter
- In contrast to a pustule, contents are clear
- Varicella zoster makes vesicles
- Bulla is over 0.5 cm diamter
- Look differently depending on where the fluid resides: under the stratum corneum or under the whole epidermis
- Vesicles:
- Bullae:
[edit] Secondary Lesions
- Lesions that evolve from pt interaction with a disease process: scratching, picking, et cetera
[edit] Scales
- Excess dead epidermal cells that are produced by abnormal keratinization and shedding





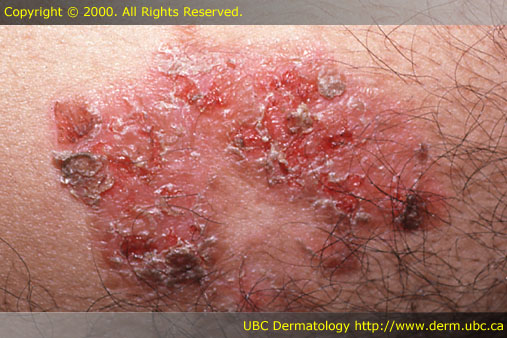
[edit] Crusts (scab) / Erosions
- Crust: collection of dried serum and cellular debris (a scab)
- Erosion: focal loss of epidermis
- Any scratch that doesn't scar
- Do not penetrate below the dermal-epidermal junction and thus do not scar



[edit] Escoriations
- Erosion caused by scratching
- Often linear
[edit] Ulcers
- A focal loss of epidermis and dermis
- Ulcers heal with scarring





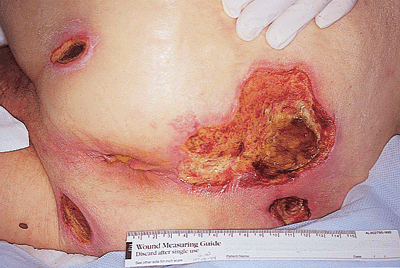
[edit] Fissure
- Linear loss of epidermis and dermis with sharply defined, vertical walls
- Chapped lips, for example
- Think of corners of mouth





[edit] Atrophy
- Depression in the skin from thinning of the epidermis or dermis
- feels like cigarette paper
- morvea: localized scleroderma
- http://mizzouderm.com/uploads/4/4/2/3/4423869/4212698_orig.jpg?214

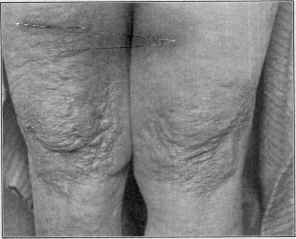
[edit] Scar
- Abnormal form of connective tissue implying dermal damage.
- After an injury scars are initially thick and pink and become white and atrophic with time.
- To scar, one must get to the dermal papillary level, to the erector pili muscle.
- One year until the scar looks like it's final product

[edit] Special Lesions
[edit] Comedone
- Plug of subaceous and keratinaceous debris lodged in the opening of an hair follicle.
- The follicle opening may be widened (blackhead) or narrowed (whitehead).
- A type of acne.





[edit] Lichenifcation
- Area of thickened epidermis induced by scratching.
- These pts did it to themselves.
- Skin lines are accentuated so that the surface looks like a washboard
- How many times do you have to scratch yourself to induce lichenification: 200k scratches / rubs to get this response!


[edit] Burrow
- Narrow, elevated tortuous channel in the skin, created by a parasite
- Scabies most common

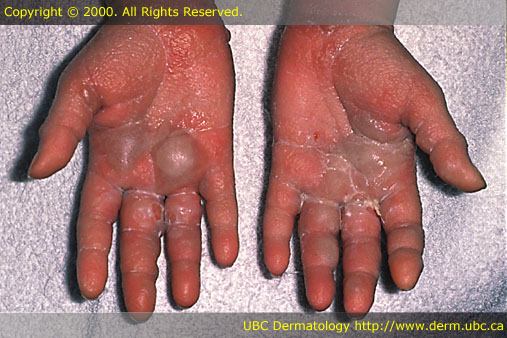
[edit] Milia
- Small cysts under the skin; have walls containing epidermis
- Associated with scarring; when skin is scarring from injury, skin may form milia
- Porphyria can occur secondary to hepatitis C; makes skin of hands fragile, thus producing milia




[edit] Cyst
- Circumscribed with wall and lumen; may contain solid matter or fluid
- A larger milia

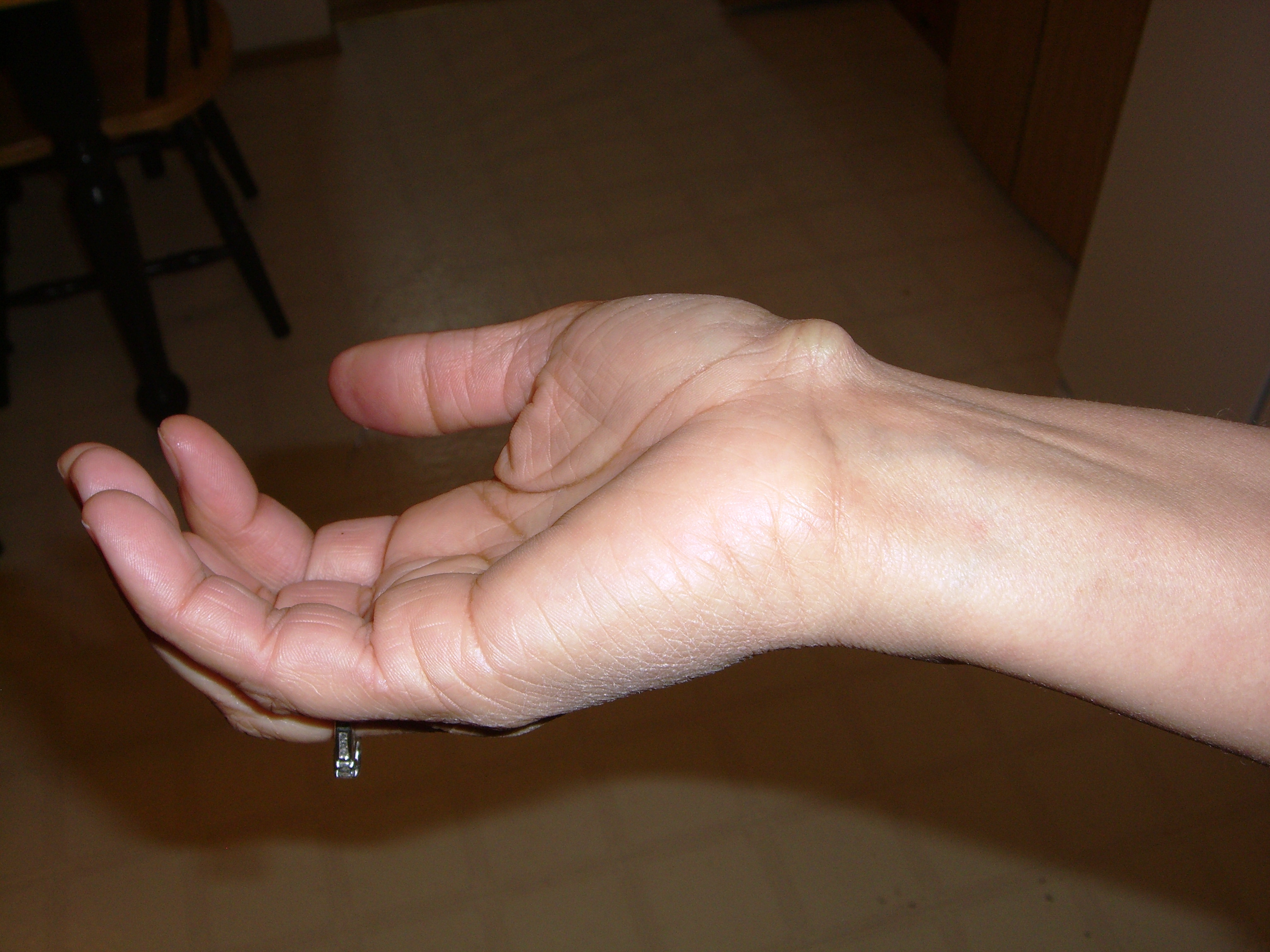




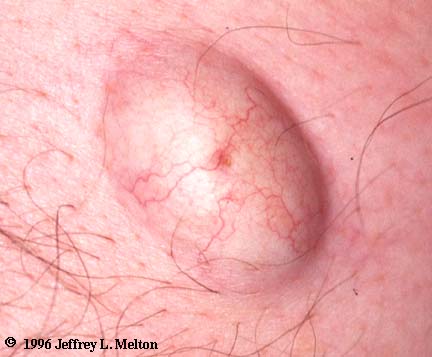
[edit] Telangiectasia
- Dilated superficial blood vessels
- Can indicate liver disease
- Also called spider angiomas is a form of telangiectasias with a lesion



- http://www.nytimes.com/imagepages/2007/08/01/health/adam/2998Telangiectasialegs.html
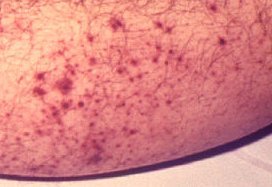
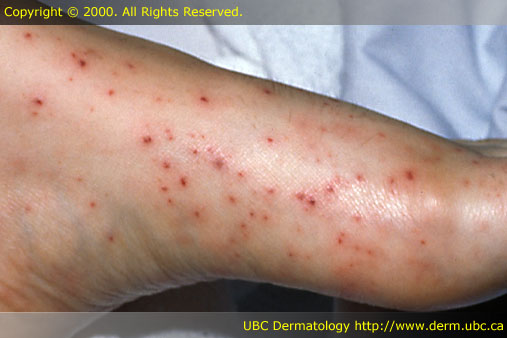
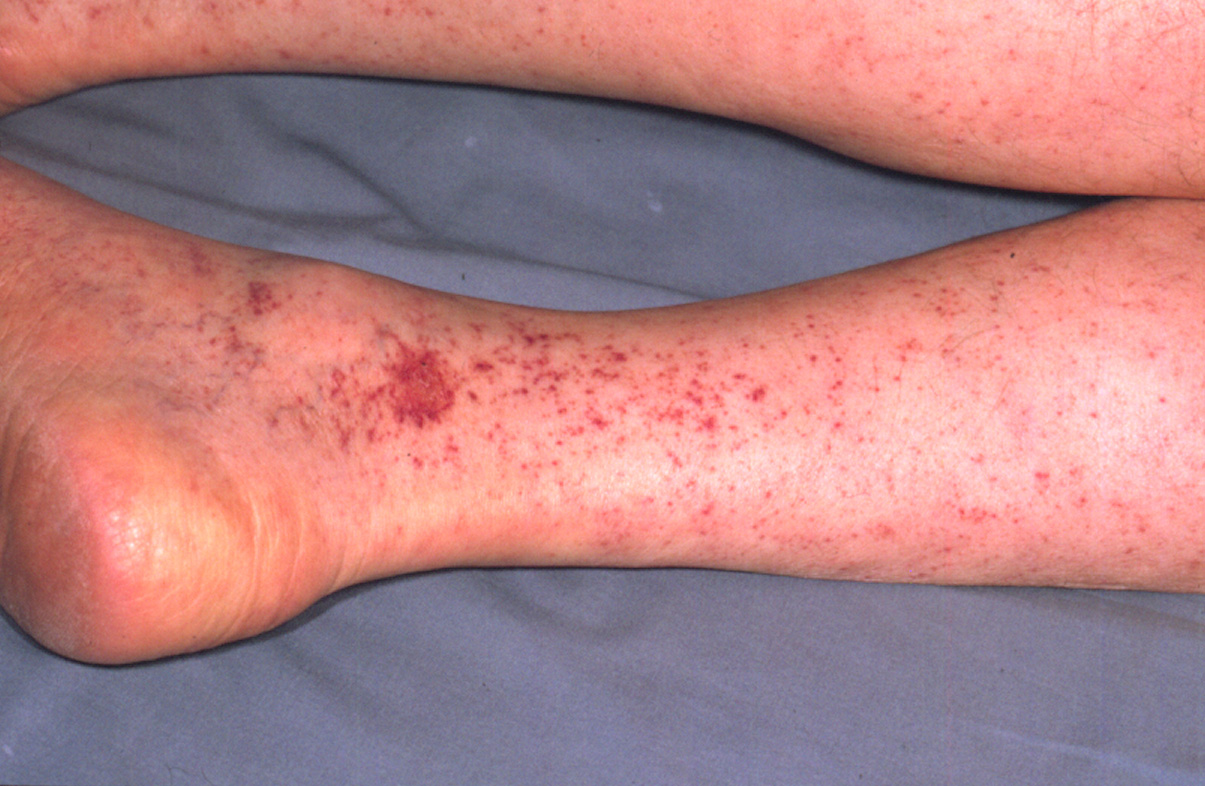
[edit] Petechiae / Purpura
- Petechiae: circumscribed deposit of blood, < 0.5 cm diameter
- Purpura: circumscribed deposit of blood, > 0.5 cm diameter
- Petechiae
- Purpura:
[edit] Examples
- Vitiligo: white macule at the nasal bridge, right edge of the nose, and inferior medial border of the right eye
- Port-wine stain: red macule across the distributuion of trigeminal V2
- Lichen planus: collection of papules forming a plaque on the right hand and wrist, linear in distribution
- Deep hemangioma: 2 cm tumor at the lateral, inferior border of the left eye, lacks ulceration, telangeictasia, or eruption