American Coot
From Devonshire
(→External links) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
* [http://www.birds.cornell.edu/AllAboutBirds/BirdGuide/American_Coot.html American Coot] - Cornell Lab of Ornithology. | * [http://www.birds.cornell.edu/AllAboutBirds/BirdGuide/American_Coot.html American Coot] - Cornell Lab of Ornithology. | ||
| - | [[Category: Animals]] [[Category: Birds]] | + | [[Category: Animals|Rail, American Coot]] |
| + | [[Category: Birds|Rail, American Coot]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Wildlife of the Glennshire River|Rail, American Coot]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Least Concern species|Rail, American Coot]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Gruiformes|Rail, American Coot]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Rallidae|Coot, American Coot]] | ||
Current revision as of 23:58, 7 July 2009
The American Coot (Fulica americana) is a bird of the family Rallidae, inhabiting wetlands and open water bodies. About 16 inches (40 cm) in length and weighing 1.4 lb (0.65 kg), adults have a short thick white bill and white frontal shield, which usually has a reddish-brown spot near the top of the bill between the eyes. From up close, a dark band can be distinguished at the billtip. The body is grey with the head and neck darker than the rest of the body. Their legs are yellowish, with scalloped toes rather than webbed feet. Their chicks have black bodies with bright red head and beak, and orange plumes around the neck. The call is a high-pitched squeaking honk somewhat like a goose's but more hollow sounding.

Contents |
Range
Their breeding habitat is marshes from southern Quebec to the Pacific coast of North America and as far south as northern South America. Birds from temperate North America east of the Rocky Mountains migrate to the southern United States and southern British Columbia. They are often year-round residents where water remains open in winter. It is notable that e.g. in Ohio, birds apparently move to their breeding range about half a month earlier and leave for winter quarters the same time later than they did 100 years ago. Also, the number of birds that stay year-round near the northern limit of the species' range seems to be increasing, perhaps an effect of global warming.
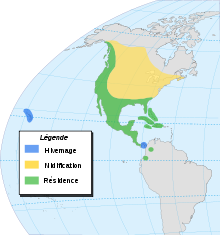
- Yellow = Breeding only
- Green = All-year
- Blue = Wintering only.
Although coots seem rather weak fliers, like most rails they have considerable stamina once airborne. This species has crossed the Atlantic to reach western Europe at least 23 times since records beganTemplate:When, including 12 records in the Azores and four in Great Britain. In December 2003, an individual of this species attempted to overwinter in the Shetland Islands, Scotland.
Ecology
These chunky birds require a great deal of effort to become airborne, pedaling across the water with their feet before lifting off. The way in which their heads bob when they walk or swim has earned them the name "marsh hen"or "mud hen".
These birds are frequently seen swimming in open water. They can dive for food but can also forage on land. American Coots are omnivorous, eating plant material, arthropods, fish, and other aquatic animals. They nest in a well-concealed location in tall reeds.
American Coots are highly territorial during the breeding season, with both males and females fighting with neighbors to maintain a small territory where they obtain all their food. The females are known to lay eggs in neighbors' nests (conspecific brood parasitism); contrary to what one might expect, this behavior is more common among females that already have a nest than among those that were not able to secure a suitable territory for breeding in that season.
Outside the breeding season, particularly in winter, they gather together in sometimes huge groups for protection and socializing. Groups of coots are called covers or rafts.
On the Louisiana coast, the Cajun word for coot is pouldeau, from French for "coot", poule d'eau - literally "water hen".
Fossil record
Coot fossils from the Middle Pleistocene of California have been described as Fulica hesterna but cannot be separated from the present-day American Coot<ref>Olson (1974)</ref>. However, the Pleistocene coot Fulica shufeldti (formerly F. minor), famously known as part of the Fossil Lake fauna, quite possibly was a paleosubspecies of the American Coot (as Fulica americana shufeldti) as they only differed marginally in size and proportions from from living birds. Thus, it seems that the modern-type American Coots evolved during the mid-late Pleistocene, a few 100,000 years ago.
References
See Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/American_Coot
External links
- American Coot - Fulica americana - USGS Patuxent Bird Identification InfoCenter.
- American Coot information and photos - South Dakota Birds and Birding.
- American Coot - Cornell Lab of Ornithology.
