Chap2:Introduction to Routers
From Mycomputer Notes
A router also needs an Operating System (O/S)to properly function, as any other computer. On a router the Operating System (OS) is called IOS developped by CISCO
Contents |
[edit] Internetwork Operating System (IOS)
The CISCO IOS provides the following network procedures:
- Basic Routing & switching functions
- Reliable & secured access to network resources
- Network Scalability
[edit] Command Line Environment (CLI)
Commands are entered like in DOS or Unix/Linux. This commands offered the following avantages:
- Command completion
- Syntax verification
- Help Levels
- Keyboard shortcuts
The Cisco CLI uses a hierarchical structure. This structure requires entry into different modes to accomplish particular tasks. For example, to configure a router interface, the user must enter interface configuration mode. All configurations that are entered in interface configuration mode apply only to that interface. Each configuration mode is indicated with a distinctive prompt and allows only commands that are appropriate for that mode.
As a security feature the Cisco IOS software separates the EXEC sessions into two access levels. These levels are user:
- EXEC mode
- Privileged EXEC mode
The privileged EXEC mode is also known as enable mode. The following are the features of the user EXEC mode and privileged EXEC mode:
- user EXEC mode
- allows only a limited number of basic monitoring commands. This is often referred to as a view only mode. The user EXEC level does not allow any commands that might change the configuration of the router. The user EXEC mode can be identified by the > prompt
- privileged EXEC mode
- provides access to all router commands. This mode can be configured to require a password. For added protection, it can also be configured to require a user ID. This allows only authorized users to access the router. Configuration and management commands require that the network administrator be at the privileged EXEC level. Global configuration mode and all other more specific configuration modes can only be reached from the privileged EXEC mode. The privileged EXEC mode can be identified by the # prompt.

|
[edit] IOS Software Features
Cisco continues to develop different IOS software images to optimize the Cisco IOS software that these various platforms require. Each IOS image represents a different feature set that serves the various
- Device Platforms
- Available Memory Ressources
- Customer Needs
The naming convention for the different Cisco IOS releases contains three parts:
- The platform on which the image runs = xxxx
- The special features supported in the image = yyyy
- Where the image runs and whether it has been zipped or compressed = ww
One of the main considerations when selecting a new IOS image is compatibility with the router flash and RAM memory. In general, the newer the release and the more features that it provides, the more flash and RAM memory it requires. Use the show version command on the Cisco device to check the current image and available flash.
Before installing a new Cisco IOS software image on the router, check to see if the router meets the RAM memory and flash requirements for that image. To see the amount of RAM, issue the show version command
[edit] Operating CISCO IOS Software
The Cisco IOS devices have three distinct operating environments or modes:
- ROM monitor
- Boot ROM
- Cisco IOS

|
At startup, a Cisco router normally loads into RAM and executes one of these operating environments. A system administrator can use the configuration register setting to control the default startup mode for a router.
ROM Monitor performs the bootstrap process :
- Provides low-level functionality and diagnostic
- Used to recover from system failures and to recover a lost password.
- CAN NOT be accessed thorugh any of the network interfaces, but only through a console port session.
When the Router is running in the Rom Monitor Mode:
- Only a limited subset of the Cisco IOS software feature set is available.
- This Mode allows write operations to Flash Memory
(used primarily to replace the Cisco IOS software image that is stored in Flash)
- Cisco IOS Software Image can be modified in boot ROOM mode by using the copy tftp flash command
The normal operation of a router requires use of the full Cisco IOS image as stored in flash. In some devices, the IOS is executed directly from flash. However, most Cisco routers require a copy of the IOS to be loaded into RAM and also executed from RAM. Some IOS images are stored in flash in a compressed format and have to be expanded when copied to RAM.
To see the IOS image and version that is running, use the show version command, which also indicates the configuration register setting. The show flash command is used to verify that the system has sufficient memory to load a new Cisco IOS
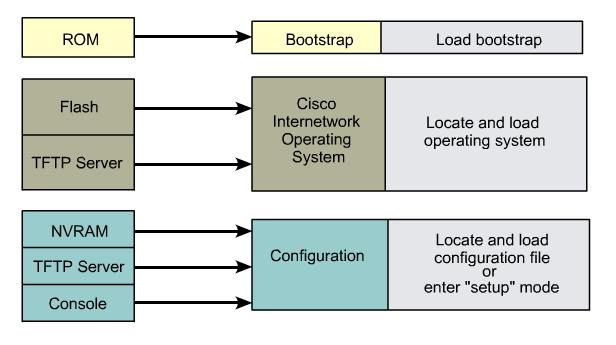
Three sources for the IOS By default and in order
- Flash
- TFTP*
- ROM
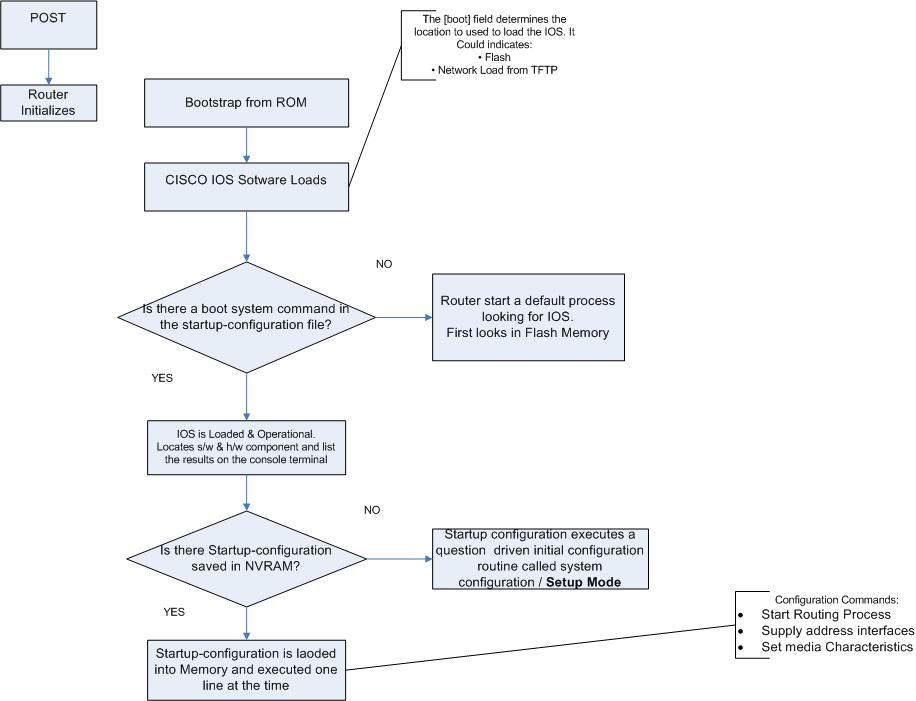
[edit] Starting a Router
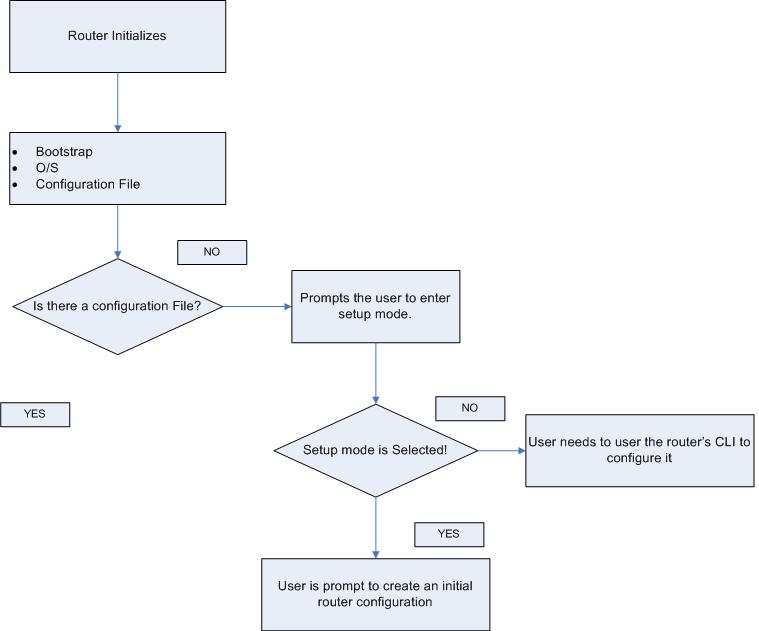
A router initializes by loading the bootstrap, the operating system, and a configuration file. If the router cannot find a configuration file, it enters setup mode. Upon completion of the setup mode, a backup copy of the configuration file may be saved to NVRAM.
Router Startup sequence
|
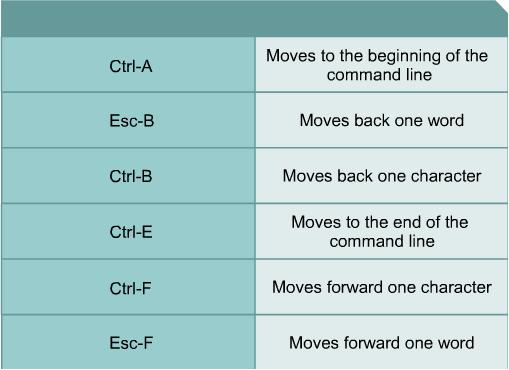
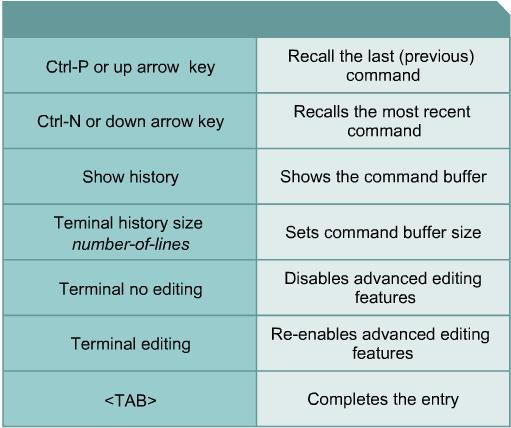
[edit] CLI Keyboard Shortcuts
The key sequences indicated in the picture below can be used to move the cursor on the command line for corrections or changes.
Although enhanced editing mode is automatically enabled with the current software release, it can be disabled if it interferes with the interaction of written scripts. To disable enhanced editing mode, type terminal no editing at the privileged EXEC mode prompt.
|
The user interface provides a history or record of commands that have been entered. This page will explain the use and benefits of this feature. This feature is particularly useful for recalling long or complex commands or entries. The command history feature can be used to perform the following tasks:
- Set the command history buffer size
- Recall commands
- Disable the command history feature
|
The show version command. This command displays information about the Cisco IOS software version that is installed on the router. This includes the configuration register and the boot field settings.
Information from the show version command:
- IOS version and descriptive information
- Bootstrap ROM version
- Boot ROM version
- Router up time
- Last restart method
- System image file and location
- Router platform
- Configuration register setting
Use the show version command to identify a router IOS image and boot source.
[edit] External Ressources
For a full explanation of the commands please visite the Cisco IOS Interface Command Reference, Release 12.1