GSK3 Inhibition
From Vinodksingh
(→GOR4 result for : UNK_163320) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | =Overview= | ||
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) has recently emerged, in the field of medicinal chemistry, as one of the most attractive therapeutic targets for the development of selective inhibitors as promising new drugs for numerous serious pathologies, including Alzheimer's disease, stroke, bipolar disorders, chronic inflammatory processes, cancer, alopepia and Type II diabetes. The full potential of GSK-3 inhibitors is yet to be realised and the number of drug candidates being developed by both academic centres and pharmaceutical companies has increased exponentially in the last three years. This review discloses recent discoveries on peptides and small molecules targeting GSK-3. Antisense therapy for the modulation of GSK-3 expression is also discussed. Focusing attention on this exciting target could thus reap considerable clinical and economic rewards. | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) has recently emerged, in the field of medicinal chemistry, as one of the most attractive therapeutic targets for the development of selective inhibitors as promising new drugs for numerous serious pathologies, including Alzheimer's disease, stroke, bipolar disorders, chronic inflammatory processes, cancer, alopepia and Type II diabetes. The full potential of GSK-3 inhibitors is yet to be realised and the number of drug candidates being developed by both academic centres and pharmaceutical companies has increased exponentially in the last three years. This review discloses recent discoveries on peptides and small molecules targeting GSK-3. Antisense therapy for the modulation of GSK-3 expression is also discussed. Focusing attention on this exciting target could thus reap considerable clinical and economic rewards. | ||
| - | + | == GSK3beta== | |
| - | + | ===Structural details === | |
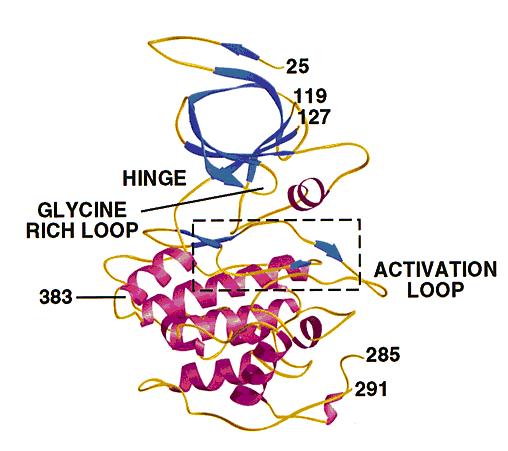
* GSK3 has the typical two-domain kinase fold with a beta-strand domain (residues 25−138) at the N-terminal end and an alpha-helical domain at the C-terminal end (residues 139−343). | * GSK3 has the typical two-domain kinase fold with a beta-strand domain (residues 25−138) at the N-terminal end and an alpha-helical domain at the C-terminal end (residues 139−343). | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
* The beta-strand domain consists of seven antiparallel beta-strands: strands 2−6 form a -barrel that is interrupted between strand 4 and 5 by a short helix (residue 96−102) that packs against the beta-barrel. | * The beta-strand domain consists of seven antiparallel beta-strands: strands 2−6 form a -barrel that is interrupted between strand 4 and 5 by a short helix (residue 96−102) that packs against the beta-barrel. | ||
* This helix is conserved in all kinases, and two of its residues play key roles in the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Arg 96 is involved in the alignment of the two domains. Glu 97 is positioned in the active site and forms a salt bridge with Lys 85, a key residue in catalysis. | * This helix is conserved in all kinases, and two of its residues play key roles in the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Arg 96 is involved in the alignment of the two domains. Glu 97 is positioned in the active site and forms a salt bridge with Lys 85, a key residue in catalysis. | ||
| + | |||
[[image:Gsk3.JPG]] | [[image:Gsk3.JPG]] | ||
| - | ''' | + | '''The structure of GSK3 .''': The N-terminal domain (blue) corresponds to the -strand domain and encompasses residue 25−138. -strand 1 was only visible in one of the two molecules in the asymmetric unit and makes hydrogen bonds with -strand 2, although it is not part of the -barrel. The -helical domain (magenta) corresponds to residues 139−349. Key features of the kinase fold such as the hinge, glycine-rich loop and activation loop are indicated. The area in the box is shown in detail in Fig. 3a and 4. Residues 7−24, 120−126 (in molecule A), 286−300 (in molecule A), 286−290 (in molecule B) and 384−420 were disordered and have not been included in the model. The side chains of residues 31, 33−35 and 37 were not visible, and these residues were modeled as glycine. Residues 46, 91−93, 121−124 and 308 were modeled as alanines. The carbons in A and B chains have a root mean square (r.m.s.) deviation of 0.48 Å after superposition. |
| + | |||
| + | ===Phosphorylation=== | ||
* GSK3 has two phosphorylation sites that influence the catalytic activity of the protein. | * GSK3 has two phosphorylation sites that influence the catalytic activity of the protein. | ||
** Ser 9 is the phosphorylation site for AKT, and the phosphorylation of this residue inactivates GSK3. | ** Ser 9 is the phosphorylation site for AKT, and the phosphorylation of this residue inactivates GSK3. | ||
** Phosphorylation of Tyr 216, located on the activation loop, increases the catalytic activity. | ** Phosphorylation of Tyr 216, located on the activation loop, increases the catalytic activity. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Similarity=== | ||
| + | * Ser/Thr protein kinase family. GSK-3 subfamily. | ||
| + | * Contains 1 protein kinase domain. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Amino Acid Sequence=== | ||
| + | The sequence GSK3B_HUMAN consists of 420 amino acids. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 10 20 30 40 50 60 | ||
| + | MSGRPRTTSF AESCKPVQQP SAFGSMKVSR DKDGSKVTTV VATPGQGPDR PQEVSYTDTK | ||
| + | |||
| + | 70 80 90 100 110 120 | ||
| + | VIGNGSFGVV YQAKLCDSGE LVAIKKVLQD KRFKNRELQI MRKLDHCNIV RLRYFFYSSG | ||
| + | |||
| + | 130 140 150 160 170 180 | ||
| + | EKKDEVYLNL VLDYVPETVY RVARHYSRAK QTLPVIYVKL YMYQLFRSLA YIHSFGICHR | ||
| + | |||
| + | 190 200 210 220 230 240 | ||
| + | DIKPQNLLLD PDTAVLKLCD FGSAKQLVRG EPNVSYICSR YYRAPELIFG ATDYTSSIDV | ||
| + | |||
| + | 250 260 270 280 290 300 | ||
| + | WSAGCVLAEL LLGQPIFPGD SGVDQLVEII KVLGTPTREQ IREMNPNYTE FKFPQIKAHP | ||
| + | |||
| + | 310 320 330 340 350 360 | ||
| + | WTKVFRPRTP PEAIALCSRL LEYTPTARLT PLEACAHSFF DELRDPNVKL PNGRDTPALF | ||
| + | |||
| + | 370 380 390 400 410 420 | ||
| + | NFTTQELSSN PPLATILIPP HARIQAAAST PTNATAASDA NTGDRGQTNN AASASASNST | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Others Details=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Molecular weight: 46744.3 | ||
| + | * Theoretical pI: 8.98 | ||
| + | * Amino acid composition: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ala (A) 34 8.1% | ||
| + | Arg (R) 27 6.4% | ||
| + | Asn (N) 17 4.0% | ||
| + | Asp (D) 22 5.2% | ||
| + | Cys (C) 9 2.1% | ||
| + | Gln (Q) 18 4.3% | ||
| + | Glu (E) 19 4.5% | ||
| + | Gly (G) 22 5.2% | ||
| + | His (H) 7 1.7% | ||
| + | Ile (I) 20 4.8% | ||
| + | Leu (L) 37 8.8% | ||
| + | Lys (K) 23 5.5% | ||
| + | Met (M) 5 1.2% | ||
| + | Phe (F) 18 4.3% | ||
| + | Pro (P) 31 7.4% | ||
| + | Ser (S) 32 7.6% | ||
| + | Thr (T) 30 7.1% | ||
| + | Trp (W) 2 0.5% | ||
| + | Tyr (Y) 18 4.3% | ||
| + | Val (V) 29 6.9% | ||
| + | Asx (B) 0 0.0% | ||
| + | Glx (Z) 0 0.0% | ||
| + | Xaa (X) 0 0.0% | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Total number of negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu): 41 | ||
| + | * Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys): 50 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Atomic composition: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Carbon C 2085 | ||
| + | Hydrogen H 3285 | ||
| + | Nitrogen N 575 | ||
| + | Oxygen O 618 | ||
| + | Sulfur S 14 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Formula: C2085H3285N575O618S14 | ||
| + | * Total number of atoms: 6577 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Extinction coefficients:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ** Extinction coefficients are in units of M-1 cm-1, at 280 nm. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *** Ext. coefficient 38320 | ||
| + | *** Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 0.820, assuming ALL Cys residues appear as half cystines | ||
| + | |||
| + | *** Ext. coefficient 37820 | ||
| + | *** Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 0.809, assuming NO Cys residues appear as half cystines | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Estimated half-life: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ** The N-terminal of the sequence considered is M (Met). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ** The estimated half-life is: 30 hours (mammalian reticulocytes, in vitro). | ||
| + | >20 hours (yeast, in vivo). | ||
| + | >10 hours (Escherichia coli, in vivo). | ||
| + | * Instability index: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ** The instability index (II) is computed to be 29.32 | ||
| + | ** This classifies the protein as stable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Aliphatic index: 81.05 | ||
| + | * Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY): -0.319 | ||
| + | |||
| + | === GOR4 result for : UNK_163320=== | ||
| + | [[image:Gsk3-gore_result.JPG]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
---- | ---- | ||
Current revision as of 06:16, 14 July 2006
Contents |
Overview
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) has recently emerged, in the field of medicinal chemistry, as one of the most attractive therapeutic targets for the development of selective inhibitors as promising new drugs for numerous serious pathologies, including Alzheimer's disease, stroke, bipolar disorders, chronic inflammatory processes, cancer, alopepia and Type II diabetes. The full potential of GSK-3 inhibitors is yet to be realised and the number of drug candidates being developed by both academic centres and pharmaceutical companies has increased exponentially in the last three years. This review discloses recent discoveries on peptides and small molecules targeting GSK-3. Antisense therapy for the modulation of GSK-3 expression is also discussed. Focusing attention on this exciting target could thus reap considerable clinical and economic rewards.
GSK3beta
Structural details
- GSK3 has the typical two-domain kinase fold with a beta-strand domain (residues 25−138) at the N-terminal end and an alpha-helical domain at the C-terminal end (residues 139−343).
- The ATP-binding site is at the interface of the alpha-helical and beta-strand domain and is bordered by the glycine-rich loop and the hinge.
- The activation loop (residues 200−226) runs along the surface of the substrate binding groove.
- The C-terminal 39 residues (residues 344−382) are outside the core kinase fold and form a small domain that packs against the alpha-helical domain.
- The beta-strand domain consists of seven antiparallel beta-strands: strands 2−6 form a -barrel that is interrupted between strand 4 and 5 by a short helix (residue 96−102) that packs against the beta-barrel.
- This helix is conserved in all kinases, and two of its residues play key roles in the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Arg 96 is involved in the alignment of the two domains. Glu 97 is positioned in the active site and forms a salt bridge with Lys 85, a key residue in catalysis.
The structure of GSK3 .: The N-terminal domain (blue) corresponds to the -strand domain and encompasses residue 25−138. -strand 1 was only visible in one of the two molecules in the asymmetric unit and makes hydrogen bonds with -strand 2, although it is not part of the -barrel. The -helical domain (magenta) corresponds to residues 139−349. Key features of the kinase fold such as the hinge, glycine-rich loop and activation loop are indicated. The area in the box is shown in detail in Fig. 3a and 4. Residues 7−24, 120−126 (in molecule A), 286−300 (in molecule A), 286−290 (in molecule B) and 384−420 were disordered and have not been included in the model. The side chains of residues 31, 33−35 and 37 were not visible, and these residues were modeled as glycine. Residues 46, 91−93, 121−124 and 308 were modeled as alanines. The carbons in A and B chains have a root mean square (r.m.s.) deviation of 0.48 Å after superposition.
Phosphorylation
- GSK3 has two phosphorylation sites that influence the catalytic activity of the protein.
- Ser 9 is the phosphorylation site for AKT, and the phosphorylation of this residue inactivates GSK3.
- Phosphorylation of Tyr 216, located on the activation loop, increases the catalytic activity.
Similarity
- Ser/Thr protein kinase family. GSK-3 subfamily.
- Contains 1 protein kinase domain.
Amino Acid Sequence
The sequence GSK3B_HUMAN consists of 420 amino acids.
10 20 30 40 50 60
MSGRPRTTSF AESCKPVQQP SAFGSMKVSR DKDGSKVTTV VATPGQGPDR PQEVSYTDTK
70 80 90 100 110 120
VIGNGSFGVV YQAKLCDSGE LVAIKKVLQD KRFKNRELQI MRKLDHCNIV RLRYFFYSSG
130 140 150 160 170 180
EKKDEVYLNL VLDYVPETVY RVARHYSRAK QTLPVIYVKL YMYQLFRSLA YIHSFGICHR
190 200 210 220 230 240
DIKPQNLLLD PDTAVLKLCD FGSAKQLVRG EPNVSYICSR YYRAPELIFG ATDYTSSIDV
250 260 270 280 290 300
WSAGCVLAEL LLGQPIFPGD SGVDQLVEII KVLGTPTREQ IREMNPNYTE FKFPQIKAHP
310 320 330 340 350 360
WTKVFRPRTP PEAIALCSRL LEYTPTARLT PLEACAHSFF DELRDPNVKL PNGRDTPALF
370 380 390 400 410 420
NFTTQELSSN PPLATILIPP HARIQAAAST PTNATAASDA NTGDRGQTNN AASASASNST
Others Details
- Molecular weight: 46744.3
- Theoretical pI: 8.98
- Amino acid composition:
Ala (A) 34 8.1% Arg (R) 27 6.4% Asn (N) 17 4.0% Asp (D) 22 5.2% Cys (C) 9 2.1% Gln (Q) 18 4.3% Glu (E) 19 4.5% Gly (G) 22 5.2% His (H) 7 1.7% Ile (I) 20 4.8% Leu (L) 37 8.8% Lys (K) 23 5.5% Met (M) 5 1.2% Phe (F) 18 4.3% Pro (P) 31 7.4% Ser (S) 32 7.6% Thr (T) 30 7.1% Trp (W) 2 0.5% Tyr (Y) 18 4.3% Val (V) 29 6.9% Asx (B) 0 0.0% Glx (Z) 0 0.0% Xaa (X) 0 0.0%
- Total number of negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu): 41
- Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys): 50
- Atomic composition:
Carbon C 2085 Hydrogen H 3285 Nitrogen N 575 Oxygen O 618 Sulfur S 14
- Formula: C2085H3285N575O618S14
- Total number of atoms: 6577
- Extinction coefficients:
- Extinction coefficients are in units of M-1 cm-1, at 280 nm.
- Ext. coefficient 38320
- Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 0.820, assuming ALL Cys residues appear as half cystines
- Ext. coefficient 37820
- Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 0.809, assuming NO Cys residues appear as half cystines
- Estimated half-life:
- The N-terminal of the sequence considered is M (Met).
- The estimated half-life is: 30 hours (mammalian reticulocytes, in vitro).
>20 hours (yeast, in vivo).
>10 hours (Escherichia coli, in vivo).
- Instability index:
- The instability index (II) is computed to be 29.32
- This classifies the protein as stable.
- Aliphatic index: 81.05
- Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY): -0.319
GOR4 result for : UNK_163320