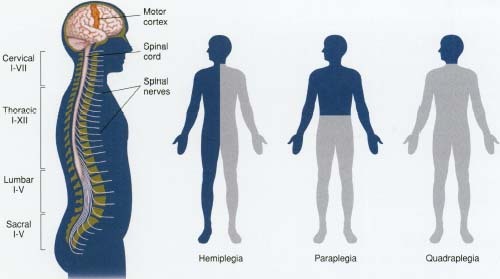
Hemiplegia
From Psy3242
Hemiplegia describes the condition of a brain damaged individual who is unable to intentionally move parts of his or her body on the side opposite that of the brain damage. Hemplegia usually occurs as a result of a loss of blood supply in the mid-cerebral artery due to aneurysm, hemorrhage, or clot. It may also be caused by a head injury, epilespy, and/or tumor. In addtion, damage to subcortical structures, such as the basal ganglia, may result in hemplegia, since such structures are often served by the mid-cerebral artery.
Resources
- NIH site
- Online encyclopedia site
- Stirling, John. Introducing Neuropsychology
- Ogden, Jenni A. Fractured Minds: A Case Study Approach to Clincial Neuropsychology