Entorhinal cortex
From Psy3242
(Difference between revisions)
Ktreynolds (Talk | contribs) |
(→Overview) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
One of the first areas to be affected by Alheimer's Disease, the '''entorhinal cortex''' plays a crucial role in memory, specifically memory consolidation (the process in which short-term memories are organized and stored as a piece of long-term memory), and memory optimization during sleep. It forms the main input to the hippocampus (commonly called the memory center). | One of the first areas to be affected by Alheimer's Disease, the '''entorhinal cortex''' plays a crucial role in memory, specifically memory consolidation (the process in which short-term memories are organized and stored as a piece of long-term memory), and memory optimization during sleep. It forms the main input to the hippocampus (commonly called the memory center). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image: cortex.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
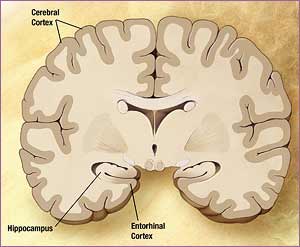
| + | This image shows the location of the Entorhinal cortex. | ||
==Sources== | ==Sources== | ||
Wikipedia | Wikipedia | ||
Revision as of 05:33, 28 April 2008
Overview
One of the first areas to be affected by Alheimer's Disease, the entorhinal cortex plays a crucial role in memory, specifically memory consolidation (the process in which short-term memories are organized and stored as a piece of long-term memory), and memory optimization during sleep. It forms the main input to the hippocampus (commonly called the memory center).
This image shows the location of the Entorhinal cortex.
Sources
Wikipedia