Prefrontal cortex
From Psy3242
Bchristian (Talk | contribs) |
Bchristian (Talk | contribs) (added picture) |
||
| (One intermediate revision not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Brain areas]] | [[Category:Brain areas]] | ||
| - | The prefrontal cortex is located in the anterior portion of the frontal lobes, which is dubbed with the term executive function as it has been thought to be used in planning complex cognitive behaviors (i.e. cognitive flexibility, abstract thinking), rule acquisition, personality expression, and moderating correct social behavior (initiating appropriate actions and inhibiting inappropriate actions. | + | The '''prefrontal cortex''' is located in the anterior portion of the '''frontal lobes''', which is dubbed with the term executive function as it has been thought to be used in planning complex cognitive behaviors (i.e. cognitive flexibility, abstract thinking), rule acquisition, personality expression, and moderating correct social behavior (initiating appropriate actions and inhibiting inappropriate actions. |
| - | The prefrontal cortex receives information from all the senses, combining the information to form useful judgments and decisions – the prefrontal cortex controls the option to “choose”. For example, an intact prefrontal cortex is able to delay immediate gratification for a better or more rewarding longer-term gratification result. Considering that the prefrontal cortex is in the fore most part of the brain, it is unfortunately susceptible to injury. | + | The '''prefrontal cortex''' receives information from all the senses, combining the information to form useful judgments and decisions – the prefrontal cortex controls the option to “choose”. For example, an intact prefrontal cortex is able to delay immediate gratification for a better or more rewarding longer-term gratification result. Considering that the prefrontal cortex is in the fore most part of the brain, it is unfortunately susceptible to injury. |
==Damage== | ==Damage== | ||
Damage to the prefrontal cortex disrupts such functions and can be seen in the example of [[Phineas Gage]], railwork worker whose prefrontal cortex was injured by a railroad spike. The resulting damage led to a change in his personality like getting into fights. | Damage to the prefrontal cortex disrupts such functions and can be seen in the example of [[Phineas Gage]], railwork worker whose prefrontal cortex was injured by a railroad spike. The resulting damage led to a change in his personality like getting into fights. | ||
| - | Some examples of weak connections between the prefrontal cortex and the rest of the brain have been seen in criminals, sociopaths, drug addicts, and people with [[schizophrenia]]; this goes to show the effect their inhibited function of the prefrontal cortex in judgments and decisions making. | + | Some examples of weak connections between the '''prefrontal cortex''' and the rest of the brain have been seen in criminals, sociopaths, drug addicts, and people with [[schizophrenia]]; this goes to show the effect their inhibited function of the '''prefrontal cortex''' in judgments and decisions making. |
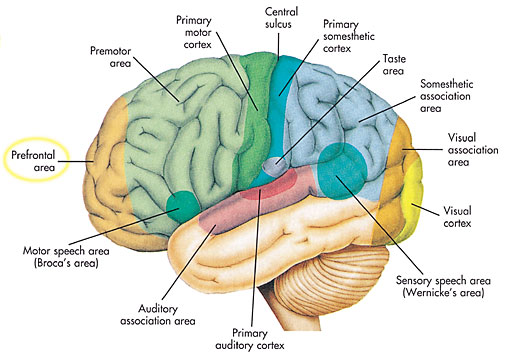
==Location== | ==Location== | ||
| - | + | [[Image:PrefrontalCortex.jpg]] | |
Current revision as of 17:58, 27 April 2008
The prefrontal cortex is located in the anterior portion of the frontal lobes, which is dubbed with the term executive function as it has been thought to be used in planning complex cognitive behaviors (i.e. cognitive flexibility, abstract thinking), rule acquisition, personality expression, and moderating correct social behavior (initiating appropriate actions and inhibiting inappropriate actions.
The prefrontal cortex receives information from all the senses, combining the information to form useful judgments and decisions – the prefrontal cortex controls the option to “choose”. For example, an intact prefrontal cortex is able to delay immediate gratification for a better or more rewarding longer-term gratification result. Considering that the prefrontal cortex is in the fore most part of the brain, it is unfortunately susceptible to injury.
Damage
Damage to the prefrontal cortex disrupts such functions and can be seen in the example of Phineas Gage, railwork worker whose prefrontal cortex was injured by a railroad spike. The resulting damage led to a change in his personality like getting into fights.
Some examples of weak connections between the prefrontal cortex and the rest of the brain have been seen in criminals, sociopaths, drug addicts, and people with schizophrenia; this goes to show the effect their inhibited function of the prefrontal cortex in judgments and decisions making.