Managing Cisco IOS Software
From Mycomputer Notes
A Cisco router cannot operate without the Cisco IOS. Each Cisco router has a predetermined bootup sequence for locating and laoding the IOS. The startup routines main purpose is to startup the router operations in a relaible manner. To accomplish this the router must:
- Test the router's hardware.
- Find and load the Cisco IOS Software.
- Find and apply configuration statements such as protocol functions and interface addresses.
[edit] Locating and loading the IOS
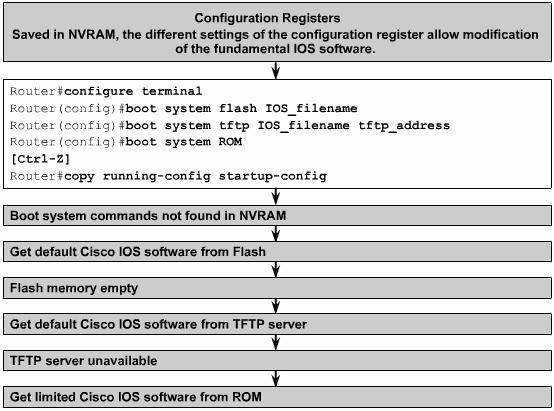
The default source for Cisco IOS Software starup depends on the hardware platform. Most routers use the boot system commands saved in NVRAM. Cisco IOS software allows several alternatives to be used. Other sources can be specified for the software, or the router can use its own fallback sequence to load the software
Router own's fallback sequence in the one illustrated on the previous image; I)Flash, II) TFTP Server III) ROM.
The settings in the configuration register enable the following alternatives:
- Global configuration mode boot system commands can be specified to enter fallback sources for a router to use in sequence. The router will use these commands as needed when it restarts.
- If NVRAM lacks boot system commands that a router can use, the system will use the Cisco IOS software in flash memory by default.
- If flash memory is empty, a router will try to use TFTP to load an IOS image from the network. The router will use the configuration register value to form a filename from which to boot a default system image that is stored on a network server.
- If a TFTP server is unavailable, the router will load the limited version Cisco IOS software image stored in ROM.
- Flash memory - A system image can be loaded from flash memory. Information stored in flash memory is not vulnerable to network failures that can occur when system images are loaded from TFTP servers.
- Network server - If flash memory is corrupted, a system image can be loaded from a TFTP server.
- ROM - The final bootstrap option is to boot from ROM. However, a system image in ROM is usually a subset of the Cisco IOS that lacks the protocols, features, and configurations of the full Cisco IOS. Also, if the software has been updated, a router may have an older version stored in ROM
[edit] Register Configuration
The order in which the router looks for CISCO IOS images to load depends on the boot field setting in the configuration register. The default settings can be modified by using the config-register command in the Global configuration mode.
The configuration register is a 16-bit register in NVRAM that is represented as 4 hexadecimal digits. The lowest four bits of the configuration register form the boot field. To ensure that the upper 12 bits are not changed, first use the show version command to retrieve the current values of the configuration register. Then use the config-register command and change only the value of the last hexadecimal digit.
The value of the configuration register is not displayed by the show running-config or show startup-config commands BUT ONLY BY show version.
testing for upada