Chap1:Wan and Routers
From Mycomputer Notes
(→WAN) |
(→WAN) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
*Routers offer many services, including internetworking and WAN interface ports. | *Routers offer many services, including internetworking and WAN interface ports. | ||
*Modems include interface voice-grade services, channel service units/digital service units (CSU/DSUs) that interface T1/E1 services, and Terminal Adapters/Network Termination 1 (TA/NT1s) that interface Integrated *Services Digital Network (ISDN) services. Communication servers concentrate dial in and dial out user communication. | *Modems include interface voice-grade services, channel service units/digital service units (CSU/DSUs) that interface T1/E1 services, and Terminal Adapters/Network Termination 1 (TA/NT1s) that interface Integrated *Services Digital Network (ISDN) services. Communication servers concentrate dial in and dial out user communication. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:wan.JPG|frame|thumb|WAN Services]] | ||
| + | |[[Image:wandevices.JPG|frame|thumb|WAN Devices]] | ||
| + | |[[Image:dataencap.JPG|frame|thumb|Data Link Encapsulation]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
Revision as of 17:02, 12 April 2006
A wide-area network (WAN) is a data communications network that connects user networks over a large geographical area. WANs have several important characteristics that distinguish them from LANs. In this module is about providing an overview of WAN technologies and protocols.
This module is about understanding the physical layer components of a router. This knowledge builds a foundation for other information and skills that are needed to configure routers and manage routed networks.
WAN
- WAN
- Data communications network that spans a large geographic area such as a state, province, or country. WANs often use transmission facilities provided by common carriers such as telephone companies.
These are the major characteristics of WANs:
- They connect devices that are separated by wide geographical areas.
- They use the services of carriers such as the Regional Bell Operating Companies (RBOCs), Sprint, MCI, and VPM
Internet Services, Inc. to establish the link or connection between sites.
- They use serial connections of various types to access bandwidth over large geographic areas.
Difference between a LAN & WAN
A WAN operates at the physical layer and the data link layer of the OSI reference model. It interconnects LANs that are usually separated by large geographic areas. WANs provide for the exchange of data packets and frames between routers and switches and the LANs they support.
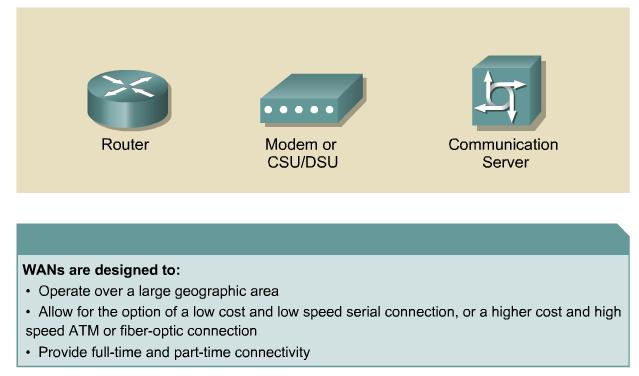
The following devices are used in WANs:
- Routers offer many services, including internetworking and WAN interface ports.
- Modems include interface voice-grade services, channel service units/digital service units (CSU/DSUs) that interface T1/E1 services, and Terminal Adapters/Network Termination 1 (TA/NT1s) that interface Integrated *Services Digital Network (ISDN) services. Communication servers concentrate dial in and dial out user communication.
File:Wandevices.JPG WAN Devices |