Lan switching
From Mycomputer Notes
(→Network Latency) |
|||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
*Using available bandwidth more efficiently | *Using available bandwidth more efficiently | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
Revision as of 00:28, 14 March 2006
Ethernet is a shared Media meanning that only one node can transmit data at any given time. The more nodes are added the more the demand of the bandwith will increase. The more nodes are added to the the media(wire) the higher the probability of collisions to occur and retramissions will increase.
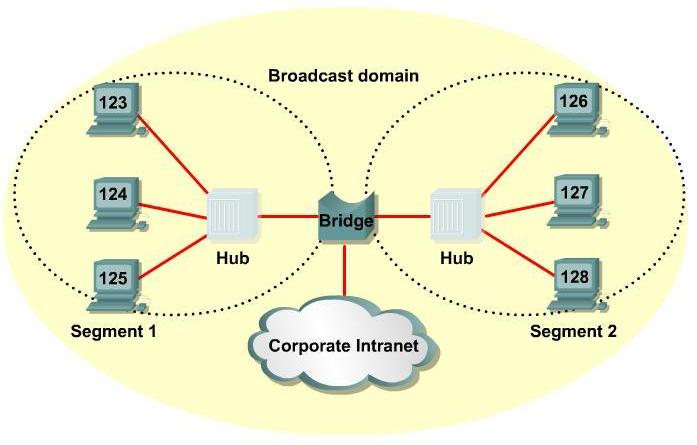
A solution when adding more nodes is to break large segments into parts and separate them into different collision domains. This can be accomplished through Bridges and swithces. With a bridge this is possible because the device keeps a table of MAC addresses and the associated ports. Normally a bridge has only 2 ports and divides a collision domain into to parts.
A Bridge will:
- Divide a collision domain NOT effect on logical or broadcast domain
- Creates morcollision domains NOT add broadcast domains.
Switching Operation
A switch is a fast multi port bridge that will create more collisions domain but smaller collision domains. Each port on the switch is it own collision domains. A switch dynamically builds and maintains a content-addressable memory (CAM) table, which holds all of the necessary MAC information for each port. Each port on the switch that connect to a host IS creating it own segment or collision domain. These physical segment is called microsegment.
When only two nodes are connected to the switch (i.e 1 host --> to the switch) other possibilities emerges. With a UTP cable one pair is used to carry the transmitted signal from one node to the other node. A separate pair is used for the return or received signal. Since only two nodes are communicating at the same time it is possible for signals to pass through both pairs simultaneously.
The ability to communicate in both directions at once is known as full duplex. Most switches are capable of supporting full duplex, as are most NICs. In full duplex mode, there is no contention for the media. A collision domain no longer exists. In theory, the bandwidth is doubled when full duplex is used.
Poperties of half duplex - Only one host can transmit at a time becayse the NIC needs to listeen for collisions.
The NIC provides several circuit.ost important are:
- received (RX)
- transmit (TX)
- Collision Detection
- Banwith usage = 50% to 60%
CSMA/CD
The first device to detect the collision will generate a jam signal (colliding devices continue to transmit so that all devices will hear the collision)
- Network Congestions:
- Relieving congestion requires
- Increasing the amount of bandwidth and/or
- Using available bandwidth more efficiently
- Bridge stores the entire frame before it fowards it. (store-and-forward)
- Symmetric switching
- provides switched connections between ports with the same bandwidth (10/10 Mbps or 100/100 Mbps).(can cause bottlenecks as users try to access servers on other segments)