Spain
From Kaiserreich
m |
m (minor edits, corrected links) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | | align=center font-size:95% colspan=2 | '''Anthem''' <br> | + | | align=center font-size:95% colspan=2 | '''Anthem''' <br> Marcha Real |
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | |'''Official Language''' || | + | |'''Official Language''' || Spanish |
|- | |- | ||
| - | |'''Capital''' || | + | |'''Capital''' || Madrid |
|- | |- | ||
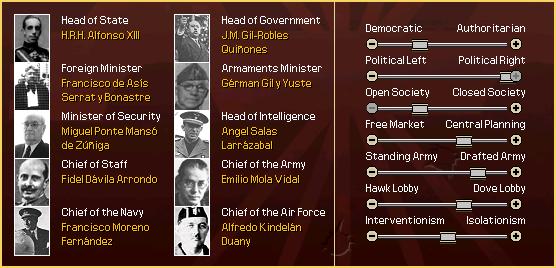
|'''Rey (King)''' || [[Alfonso XIII]] | |'''Rey (King)''' || [[Alfonso XIII]] | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
|Constitutional monarchy | |Constitutional monarchy | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | |'''Currency''' || | + | |'''Currency''' || Peseta |
|- | |- | ||
|'''Area''' | |'''Area''' | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
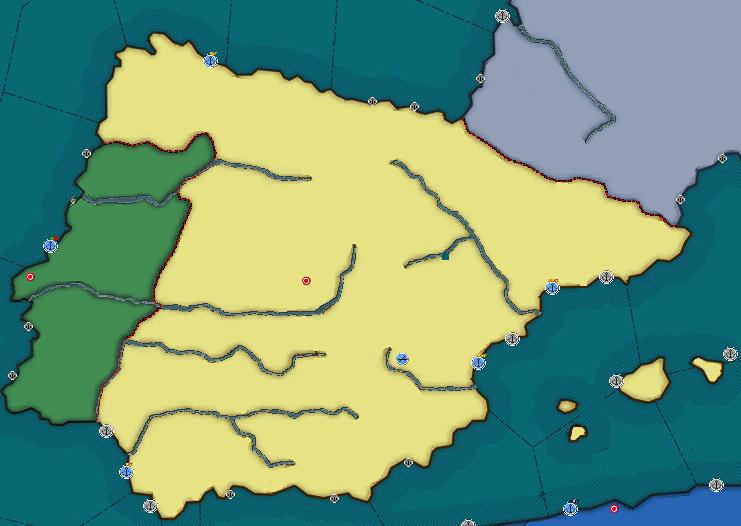
| - | '''The Kingdom of Spain''' (Official Spanish:''Reino de España'' short English form: ''Spain''; Spanish short form: ''España'') is a country in | + | '''The Kingdom of Spain''' (Official Spanish:''Reino de España'' short English form: ''Spain''; Spanish short form: ''España'') is a country in South West Europe. It borders [[Portugal]] to the west and the [[Commune of France]] to the north east. It also borders [[National France]] and [[Mittelafrika]] in Africa. |
== Politics == | == Politics == | ||
| - | Spain is ruled by a coalition of right-wing forces that supported king Alfonso's coup. However, he is not regarded as the true king by the Carlist movement which has been gaining support of some workers movements and of the | + | Spain is ruled by a coalition of right-wing forces that supported king Alfonso's coup. However, he is not regarded as the true king by the Carlist movement which has been gaining support of some workers movements and of the very religious rural population. The Anarcho-Syndicalist alliance named [[CNT-FAI|C.N.T.-F.A.I.]] has polarized the left end of the political spectrum and has been repressed by the current administration. They have the support of most workers unions and have their 'revolutionary HQs' mainly based in urban areas. |
| + | |||
[[Image:Spacab.JPG]] | [[Image:Spacab.JPG]] | ||
| Line 53: | Line 54: | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
| - | Spanish confidence was badly shaken after the war against the [[ | + | Spanish confidence was badly shaken after the war against the [[United States|United States of America]] which saw the empire lose her remaining colonies outside her immediate vicinity. Separatist movements in the Basque country and Catalonia gained support, the Church interfered in politics, and a radical workers movement destabilised the balance between conservatives and liberals. After taking the government in 1902, King [[Alfonso XIII]] showed expansionist tendencies, as demonstrated by the intervention in Morocco. The Algeciras Act of 1906 acknowledged Spanish interests in Morocco, and a protectorate over the North and South of the country was established in 1912, but it became a source of permanent unrest. |
| - | While Spain remained neutral throughout the [[Weltkrieg]], 1918 saw social tensions erupt in a number of revolts by the rural populace, right wing factions and the increasingly powerful anarcho-syndicalist movement. Alfonso XIII supported the military coup against the government by General Miguel Primo de Rivera who abolished the constitution of 1876 and installed a dictatorial rule between 1923 and 1930. He ended the uprising in Morocco with a victory over Abd el-Krim in 1926, but could not master the economic crisis and had to resign after repeated revolts by the military and students. His position was taken over by [[ | + | While Spain remained neutral throughout the [[Weltkrieg]], 1918 saw social tensions erupt in a number of revolts by the rural populace, right wing factions and the increasingly powerful anarcho-syndicalist movement. Alfonso XIII supported the military coup against the government by General Miguel Primo de Rivera who abolished the constitution of 1876 and installed a dictatorial rule between 1923 and 1930. He ended the uprising in Morocco with a victory over Abd el-Krim in 1926, but could not master the economic crisis and had to resign after repeated revolts by the military and students. His position was taken over by [[José María Gil-Robles y Quiñones]], a moderate right-wing politician. |
| - | However | + | However deep divisions remain within Spanish society in 1936. On the one hand, the resurgent [[Carlist Movement]], headed by Alfonso Carlos, aims to re-establish the "True Dynasty" and recreate an integralist Christian monarchy and on the other, the anarcho-syndicalist [[CNT-FAI]] has been inspired by the uprisings in both France and Britain to seek the abolition of the Spanish state altogether, and replace it with a voluntarist federation of communes and economic collectives. |
[[Category:Countries]] [[Category:European countries]] [[Category:Monarchies]] | [[Category:Countries]] [[Category:European countries]] [[Category:Monarchies]] | ||
Revision as of 20:47, 26 April 2009
| ||||
| Anthem Marcha Real | ||||
| Motto Plus Ultra Further Beyond | ||||
| Official Language | Spanish | |||
| Capital | Madrid | |||
| Rey (King) | Alfonso XIII | |||
| Prime Minister | José María Gil-Robles y Quiñones | |||
|
| ||||
| Establishment (De Facto) - Union of the Crowns of Aragón and Castille | 1469 | |||
| Government | Constitutional monarchy | |||
| Currency | Peseta | |||
| Area | 504,030 km² | |||
| Population | circa 35,200,737 | |||
The Kingdom of Spain (Official Spanish:Reino de España short English form: Spain; Spanish short form: España) is a country in South West Europe. It borders Portugal to the west and the Commune of France to the north east. It also borders National France and Mittelafrika in Africa.
Politics
Spain is ruled by a coalition of right-wing forces that supported king Alfonso's coup. However, he is not regarded as the true king by the Carlist movement which has been gaining support of some workers movements and of the very religious rural population. The Anarcho-Syndicalist alliance named C.N.T.-F.A.I. has polarized the left end of the political spectrum and has been repressed by the current administration. They have the support of most workers unions and have their 'revolutionary HQs' mainly based in urban areas.
History
Spanish confidence was badly shaken after the war against the United States of America which saw the empire lose her remaining colonies outside her immediate vicinity. Separatist movements in the Basque country and Catalonia gained support, the Church interfered in politics, and a radical workers movement destabilised the balance between conservatives and liberals. After taking the government in 1902, King Alfonso XIII showed expansionist tendencies, as demonstrated by the intervention in Morocco. The Algeciras Act of 1906 acknowledged Spanish interests in Morocco, and a protectorate over the North and South of the country was established in 1912, but it became a source of permanent unrest.
While Spain remained neutral throughout the Weltkrieg, 1918 saw social tensions erupt in a number of revolts by the rural populace, right wing factions and the increasingly powerful anarcho-syndicalist movement. Alfonso XIII supported the military coup against the government by General Miguel Primo de Rivera who abolished the constitution of 1876 and installed a dictatorial rule between 1923 and 1930. He ended the uprising in Morocco with a victory over Abd el-Krim in 1926, but could not master the economic crisis and had to resign after repeated revolts by the military and students. His position was taken over by José María Gil-Robles y Quiñones, a moderate right-wing politician.
However deep divisions remain within Spanish society in 1936. On the one hand, the resurgent Carlist Movement, headed by Alfonso Carlos, aims to re-establish the "True Dynasty" and recreate an integralist Christian monarchy and on the other, the anarcho-syndicalist CNT-FAI has been inspired by the uprisings in both France and Britain to seek the abolition of the Spanish state altogether, and replace it with a voluntarist federation of communes and economic collectives.