OBGYN - Normal and Abnormal Labor
From Iusmicm
(Difference between revisions)
(Created page with '=Labor: Normal, Abnormal, and Points Between= ==Definitions== *Labor: regular / rhythmic contractions, cervical dilation and effacement. **Labor is considered "preterm" if it co…') |
|||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
**Positive = >50% UC’s with late decelerations | **Positive = >50% UC’s with late decelerations | ||
**Equivocal = intermittent or late decelerations or significant variable decelerations | **Equivocal = intermittent or late decelerations or significant variable decelerations | ||
| - | |||
=====Decelerations===== | =====Decelerations===== | ||
*Early declerations: occur with cntx | *Early declerations: occur with cntx | ||
| + | **'''Non worrisome''' | ||
**Head compression leads to vagal stimulation | **Head compression leads to vagal stimulation | ||
**Recall that vagus carries parasympathetics to the heart | **Recall that vagus carries parasympathetics to the heart | ||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
*Variable Decelerations: mild, moderate, and severe. | *Variable Decelerations: mild, moderate, and severe. | ||
| + | **Lower the blood pressure the more severe. | ||
| + | **Longer the duration the more severe. | ||
| + | **'''Severity of variable decelerations are a function of blood pressure and duration''' | ||
====Sinusoidal==== | ====Sinusoidal==== | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | ===Fetal Lie, Presentation, Attitude, and Position=== | ||
*Clinical: abd palpation, auscultation of fht’s, vaginal exam | *Clinical: abd palpation, auscultation of fht’s, vaginal exam | ||
*Studies: u/s, x-ray, MRI | *Studies: u/s, x-ray, MRI | ||
| - | ===Definitions=== | + | ====Definitions==== |
| - | *Lie: relation of long axis of fetus to long axis of mother | + | *'''Lie: relation of long axis of fetus to long axis of mother''' |
**Longitudinal | **Longitudinal | ||
**Transverse | **Transverse | ||
| Line 89: | Line 93: | ||
| - | *Presentation: part foremost in the pelvis | + | *'''Presentation: part foremost in the pelvis''' |
**Cephalic | **Cephalic | ||
**Breech | **Breech | ||
**Shoulder | **Shoulder | ||
| - | + | **'''Compound:''' | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | **Compound | + | |
***Head / hand -> watch | ***Head / hand -> watch | ||
***Head / foot-> c-section | ***Head / foot-> c-section | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
*Cord prolapse (funic presentation): an '''emergency'''. | *Cord prolapse (funic presentation): an '''emergency'''. | ||
| - | *Attitude: folded on itself w/ flexed head | + | *'''Attitude: folded on itself w/ flexed head''' |
| - | **extension of head | + | **extension of head? |
| - | *Position: relation of presenting part to maternal pelvis | + | *'''Position: relation of presenting part to maternal pelvis''' |
**Cephalic -> occiput | **Cephalic -> occiput | ||
**Face -> mentum | **Face -> mentum | ||
| Line 116: | Line 115: | ||
====Fetal Attitude==== | ====Fetal Attitude==== | ||
*There are a variety of ways the fetus can present at the os; these are called attitudes: | *There are a variety of ways the fetus can present at the os; these are called attitudes: | ||
| - | **Full flexion | + | **Full flexion (A) |
| - | **Military attitude | + | **Military attitude (B) |
| - | ** | + | **Brow presentation (C) |
| - | ** | + | **Face presentation (D) |
| + | http://www.glowm.com/resources/glowm/graphics/figures/v2/0760/001f.gif | ||
| - | *Leopold’s Maneuver can be used to | + | *Leopold’s Maneuver can be used to determine the attitude of the fetus. |
| + | http://www.sciencephoto.com/image/288555/350wm/M8000133-Leopold_s_Maneuver-SPL.jpg | ||
====Vaginal Exam==== | ====Vaginal Exam==== | ||
| - | + | *Nullip versus Multip | |
| - | *Nullip Multip | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | *Station: | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | *Position: | ||
| + | *Pelvimetry: | ||
| + | **Diagonal Conjugate | ||
| + | **Ischial Spines | ||
| + | =====Pelvic Inlet===== | ||
| + | *Diagonal conjugate: >11.5 cm is adequate | ||
| + | *True obstetric conjugate = diagonal conjugate – 1.5 to 2.0 cm | ||
| + | =====Midpelvis===== | ||
| + | *Ischial spines – blunt vs. prominent | ||
| + | *Pelvic sidewalls | ||
| + | **Parallel = OK | ||
| + | **Divergent = good | ||
| + | **Convergent = bad | ||
| + | *Sacrum – hallow vs. shallow (flat) | ||
| - | + | =====Pelvic Outlet===== | |
| - | + | *Bituberous diameter > 6-8 cm | |
| - | + | *Pubic arch > 90 degrees | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | ===Stages of Labor=== | ||
| + | *1st Stage: beginning of cervical dilation to complete dilation | ||
| + | *2nd Stage: complete dilation to delivery of fetus | ||
| + | *3rd Stage: delivery of placenta (up to 30 minutes) | ||
| + | *4th Stage: first hour after delivery of placenta | ||
| + | ===Cardinal Movements of Labor====*Engagement | ||
| + | *Flexion | ||
| + | *Descent | ||
| + | *Internal rotation | ||
| + | *Extension | ||
| + | *External rotation | ||
| + | *Expulsion | ||
| + | ===Labor Curve=== | ||
| + | Interpret chart | ||
| + | ===Prolonged / Arrested Labor=== | ||
| + | *'''P'''ower: uterine contractions | ||
| + | *'''P'''elvis: adequate? | ||
| + | *'''P'''assenger: EFW, position / attitude | ||
| + | ===Dysfunctional Labor=== | ||
| + | {|border=1 | ||
| + | !Pattern | ||
| + | !Nullip | ||
| + | !Multip | ||
| + | !Rx | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Prolonged latent phase | ||
| + | |>20 hr | ||
| + | |>14 hr | ||
| + | |Rest, AROM, Pit | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Protracted dilation | ||
| + | |<1.2 cm/hr | ||
| + | |<1.5 cm/hr | ||
| + | |AROM, Pit | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Protracted descent | ||
| + | |<1 cm/hr | ||
| + | |<2 cm/hr | ||
| + | |Pit | ||
| + | !Arrest of dilation | ||
| + | |>2 hr | ||
| + | |>2 hr | ||
| + | |AROM, Pit, C/S | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Arrest of descent | ||
| + | |>2 hr | ||
| + | |>1 hr | ||
| + | |Vacuum, forceps, C/S | ||
| + | |} | ||
| - | + | ===Cesarean Section=== | |
| - | + | *History | |
| - | + | **''Caedere -> caesura'': to cut; ''seco'': to cut. | |
| - | + | **Francois Rousset (1581) | |
| - | + | **Max Sanger (1882)- Leipzig | |
| - | + | *Most common surgical procedure | |
| - | . | + | **1965 <5%, 1996 - 20.7%, 2004 - 29.1% |
| - | . | + | **No change in cerebral palsy rate |
| + | ====C-section - Techniques==== | ||
| + | *Uterine Incisions: | ||
| + | **Low transverse | ||
| + | **Low verticle | ||
| + | **Classical | ||
| + | **Kerr | ||
| + | ====C-section - Indications==== | ||
| + | =====Fetal C-section Indications===== | ||
| + | *Distress / intolerance of labor | ||
| + | *Malpresentation (breech, transverse) | ||
| + | *Twins, multiples | ||
| + | **Vtx / Vtx = allow to labor | ||
| + | *Some congenital anomalies | ||
| + | **NTD | ||
| + | =====Maternal-Fetal C-section Indications===== | ||
| + | *Arrest of active labor | ||
| + | *Failed induction of labor (?) | ||
| + | *Placenta previa, vasa previa | ||
| + | *Active HSV outbreak | ||
| + | *HIV+ (viral load >1000/ml) | ||
| + | *EFW > 4500 - 5000 gms (increasing risk of shoulder dystocia) | ||
| + | =====Maternal C-section Indications===== | ||
| + | *Obstructive tumors (some leiomyomas) | ||
| + | *Severe condylomata acuminata | ||
| + | *Cervical cancer | ||
| + | *Abdominal cerclage | ||
| + | *Prior c-section | ||
| + | *Prior vaginal colporrhaphy | ||
| + | *Vaginal delivery contraindicated medically | ||
| + | *Pregnant??? | ||
| + | ====C-section - Risks==== | ||
| + | *At time of surgery / Immediate post-op | ||
| + | *Infection: endometritis, wound infection, septic pelvic thrombophlebitis (SPT) | ||
| + | *Bleeding: transfusion, hysterectomy | ||
| + | *Damage to fetus | ||
| + | *Damage to adjacent organs | ||
| + | *Subsequent pregnancy | ||
| + | **Uterine rupture | ||
| + | **Placenta previa -> accreta | ||
| + | ***0 –> 5% | ||
| + | ***1 –> 24% | ||
| + | ***2 –> 48% | ||
| + | ***3 –> 67% | ||
| + | **Adhesions | ||
| + | ===Operative Vaginal Delivery=== | ||
| + | *Forceps and vacuum | ||
| + | ====Operative Vaginal Delivery - Classification==== | ||
| + | *Outlet: scalp visible at introitus w/out separating labia; no rotation | ||
| + | *Low: leading point of skull at or below +2 cm station | ||
| + | **Rotate < 45° | ||
| + | **Rotate > 45° | ||
| + | *Mid: above +2 cm station but engaged | ||
| - | + | ====Operative Vaginal Delivery - Indications==== | |
| - | + | *Nonreassuring FHT’s | |
| - | + | *Prolonged 2nd stage of labor | |
| - | + | *Shortened 2nd stage if pushing / Valsalva not indicated | |
| - | + | *Maternal exhaustion | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | ====Operative Vaginal Delivery - Prerequisites==== | ||
| + | *Cervix completely dilated | ||
| + | *Ruptured membranes | ||
| + | *Fetal skull engaged in pelvis | ||
| + | *Empty bladder | ||
| + | *Position! Position! Position! | ||
| + | *Adequate pelvis | ||
| + | *Adequate anesthesia | ||
| + | ====Operative Vaginal Delivery - Forceps Assisted==== | ||
| - | + | ====Operative Vaginal Delivery - Risks==== | |
| - | + | *Maternal: | |
| - | + | **Vaginal / perineal trauma, damage to rectal sphincter | |
| - | + | *Fetal: | |
| - | + | **Cephalohematoma | |
| - | + | **Subgaleal hemorrhage | |
| - | + | **Bony facial trauma | |
| - | + | **Facial nerve injury | |
| + | **Intraventricular hemorrhage | ||
| + | ===Birth Trauma=== | ||
| + | *Caput succedaneum: | ||
| + | **Very common | ||
| + | **Crosses midline | ||
| + | *Subgaleal hemorrhage: | ||
| + | **Rare | ||
| + | **Hypovolemia and DIC | ||
| + | ===Common Post Partum Problems=== | ||
| + | *PP Hemorrhage: >500cc (>1000cc for c/s): | ||
| + | **Atony | ||
| + | **Lacerations (cervix, vagina, perineum) | ||
| + | **Retained placenta | ||
| + | **Uterine rupture | ||
| + | **Uterine inversion | ||
| + | **Amniotic fluid embolism | ||
| + | *Endometritis: | ||
| + | **Fundal tenderness w/ temperature >38°C x 2 or >38.5°C | ||
| + | **Polymicrobial infection | ||
| + | **More common after c/s | ||
| + | ***Prolonged ruptured membranes | ||
| + | ***Chorioamnionitis | ||
| - | + | ====PP / Post-Op Fever==== | |
| + | *Causes and symptoms | ||
| + | **Wind (atelectasis, pneumonia) | ||
| + | **Wound (seroma, necrotizing fasciitis) | ||
| + | **Water (UTI) | ||
| + | **Walk (thrmobophlebitis) | ||
| + | **Wonder drug (drug reaction) | ||
| + | **Womb (endometriosis) | ||
| + | **Wean (mastitis, engorgement) | ||
Revision as of 20:52, 14 December 2011
Contents
|
Labor: Normal, Abnormal, and Points Between
Definitions
- Labor: regular / rhythmic contractions, cervical dilation and effacement.
- Labor is considered "preterm" if it commences before 37 weeks EGA (estimated gestational age)
- 10-12% of pregnancies include preterm labor.
- Labor is considered "postdates" if it commences after 42 weeks EGA.
- Braxton Hicks contractions are contractions of a weak or irregular nature.
Physiology of Labor
- There are many factors that play a role in the coordinated contraction of all the uterine smooth muscle for labor.
- Progesterone and Relaxin are key regulating factors in animals.
- 17alpha-hydroxyprogesterone caproate
- Gap juctions of the uterine smooth muscle are increased near term.
- Presumably to augment myofiber-myofiber communication for a well sequenced contraction.
- Oxytocin, surprisingly, shows no change in blood levels.
- Oxytocin receptors, however are elevated.
**Furthermore, there is elevated decidual production.
- Several prostaglandins are elevated for labor: PGE1, PGE2, PGF2alpha
- Mother becomes more sensitive to changes in Ca at term.
- This is presumably because the uterine muscle is storing up more and more Ca to augment contraction.
- Like prostaglandins, many cytokines are elevated: IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-alpha.
Labor and Delivery Admission
- The workup for a L&D admission includes:
- H&P
- Fetal monitoring
- Leopold’s maneuver
- Vaginal exam
- R/o (rule out) placenta previa and ROM first
- Cervical dilation / effacement / station and fetal position
Fetal Monitoring
- There are several technical methods for fetal monitoring.
- With fetal monitoring we are concerned with the baby's heart rate and the uterine pressure.
- For baby's heart rate, the baseline should be around 120-160 bpm.
- We are looking for: variability, accelerations / decelerations
- For uterine pressure (contractions) we are looking for: frequency, duration, uterine tone.
Variability and Accelerations / Decelerations
- Variability:
- Absent: 0-2 bpm
- Minimal: 3-5 bpm
- Moderate: 6-25 bpm
- Marked: saltatory, >25 bpm
- Fetal Monitoring:
- Accelerations- “15 x 15”
- Reactive fetal heart tracing (nonstress test)
- 2 accelerations in 20 minutes or less
- Contraction stress test (Oxytocin challenge test)
- 3 UC’s x 40 sec in 10 mins
- Negative = no decelerations
- Positive = >50% UC’s with late decelerations
- Equivocal = intermittent or late decelerations or significant variable decelerations
Decelerations
- Early declerations: occur with cntx
- Non worrisome
- Head compression leads to vagal stimulation
- Recall that vagus carries parasympathetics to the heart
- Late decelerations: begin at peak of cntx or after
- Fetal hypoxia is usually the culprit of late decelerations.
- Variable: can occur at any time
- Variable decelerations should raise one's suspicion for cord compression
- Variable Decelerations: mild, moderate, and severe.
- Lower the blood pressure the more severe.
- Longer the duration the more severe.
- Severity of variable decelerations are a function of blood pressure and duration
Sinusoidal
Fetal Lie, Presentation, Attitude, and Position
- Clinical: abd palpation, auscultation of fht’s, vaginal exam
- Studies: u/s, x-ray, MRI
Definitions
- Lie: relation of long axis of fetus to long axis of mother
- Longitudinal
- Transverse
- Oblique
- Presentation: part foremost in the pelvis
- Cephalic
- Breech
- Shoulder
- Compound:
- Head / hand -> watch
- Head / foot-> c-section
- Cord prolapse (funic presentation): an emergency.
- Attitude: folded on itself w/ flexed head
- extension of head?
- Position: relation of presenting part to maternal pelvis
- Cephalic -> occiput
- Face -> mentum
- Breech -> sacrum
- Transverse -> acromion process
Fetal Attitude
- There are a variety of ways the fetus can present at the os; these are called attitudes:
- Full flexion (A)
- Military attitude (B)
- Brow presentation (C)
- Face presentation (D)
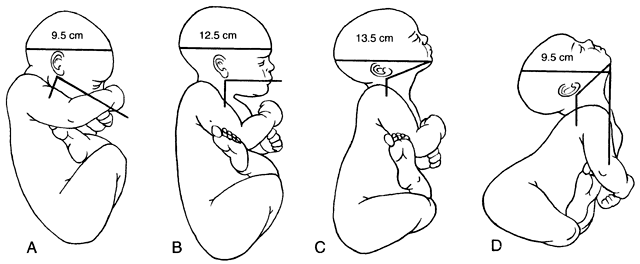
- Leopold’s Maneuver can be used to determine the attitude of the fetus.

Vaginal Exam
- Nullip versus Multip
- Station:
- Position:
- Pelvimetry:
- Diagonal Conjugate
- Ischial Spines
Pelvic Inlet
- Diagonal conjugate: >11.5 cm is adequate
- True obstetric conjugate = diagonal conjugate – 1.5 to 2.0 cm
Midpelvis
- Ischial spines – blunt vs. prominent
- Pelvic sidewalls
- Parallel = OK
- Divergent = good
- Convergent = bad
- Sacrum – hallow vs. shallow (flat)
Pelvic Outlet
- Bituberous diameter > 6-8 cm
- Pubic arch > 90 degrees
Stages of Labor
- 1st Stage: beginning of cervical dilation to complete dilation
- 2nd Stage: complete dilation to delivery of fetus
- 3rd Stage: delivery of placenta (up to 30 minutes)
- 4th Stage: first hour after delivery of placenta
===Cardinal Movements of Labor====*Engagement
- Flexion
- Descent
- Internal rotation
- Extension
- External rotation
- Expulsion
Labor Curve
Interpret chart
Prolonged / Arrested Labor
- Power: uterine contractions
- Pelvis: adequate?
- Passenger: EFW, position / attitude
Dysfunctional Labor
| Pattern | Nullip | Multip | Rx | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prolonged latent phase | >20 hr | >14 hr | Rest, AROM, Pit | ||||
| Protracted dilation | <1.2 cm/hr | <1.5 cm/hr | AROM, Pit | ||||
| Protracted descent | <1 cm/hr | <2 cm/hr | Pit | Arrest of dilation | >2 hr | >2 hr | AROM, Pit, C/S |
| Arrest of descent | >2 hr | >1 hr | Vacuum, forceps, C/S |
Cesarean Section
- History
- Caedere -> caesura: to cut; seco: to cut.
- Francois Rousset (1581)
- Max Sanger (1882)- Leipzig
- Most common surgical procedure
- 1965 <5%, 1996 - 20.7%, 2004 - 29.1%
- No change in cerebral palsy rate
C-section - Techniques
- Uterine Incisions:
- Low transverse
- Low verticle
- Classical
- Kerr
C-section - Indications
Fetal C-section Indications
- Distress / intolerance of labor
- Malpresentation (breech, transverse)
- Twins, multiples
- Vtx / Vtx = allow to labor
- Some congenital anomalies
- NTD
Maternal-Fetal C-section Indications
- Arrest of active labor
- Failed induction of labor (?)
- Placenta previa, vasa previa
- Active HSV outbreak
- HIV+ (viral load >1000/ml)
- EFW > 4500 - 5000 gms (increasing risk of shoulder dystocia)
Maternal C-section Indications
- Obstructive tumors (some leiomyomas)
- Severe condylomata acuminata
- Cervical cancer
- Abdominal cerclage
- Prior c-section
- Prior vaginal colporrhaphy
- Vaginal delivery contraindicated medically
- Pregnant???
C-section - Risks
- At time of surgery / Immediate post-op
- Infection: endometritis, wound infection, septic pelvic thrombophlebitis (SPT)
- Bleeding: transfusion, hysterectomy
- Damage to fetus
- Damage to adjacent organs
- Subsequent pregnancy
- Uterine rupture
- Placenta previa -> accreta
- 0 –> 5%
- 1 –> 24%
- 2 –> 48%
- 3 –> 67%
- Adhesions
Operative Vaginal Delivery
- Forceps and vacuum
Operative Vaginal Delivery - Classification
- Outlet: scalp visible at introitus w/out separating labia; no rotation
- Low: leading point of skull at or below +2 cm station
- Rotate < 45°
- Rotate > 45°
- Mid: above +2 cm station but engaged
Operative Vaginal Delivery - Indications
- Nonreassuring FHT’s
- Prolonged 2nd stage of labor
- Shortened 2nd stage if pushing / Valsalva not indicated
- Maternal exhaustion
Operative Vaginal Delivery - Prerequisites
- Cervix completely dilated
- Ruptured membranes
- Fetal skull engaged in pelvis
- Empty bladder
- Position! Position! Position!
- Adequate pelvis
- Adequate anesthesia
Operative Vaginal Delivery - Forceps Assisted
Operative Vaginal Delivery - Risks
- Maternal:
- Vaginal / perineal trauma, damage to rectal sphincter
- Fetal:
- Cephalohematoma
- Subgaleal hemorrhage
- Bony facial trauma
- Facial nerve injury
- Intraventricular hemorrhage
Birth Trauma
- Caput succedaneum:
- Very common
- Crosses midline
- Subgaleal hemorrhage:
- Rare
- Hypovolemia and DIC
Common Post Partum Problems
- PP Hemorrhage: >500cc (>1000cc for c/s):
- Atony
- Lacerations (cervix, vagina, perineum)
- Retained placenta
- Uterine rupture
- Uterine inversion
- Amniotic fluid embolism
- Endometritis:
- Fundal tenderness w/ temperature >38°C x 2 or >38.5°C
- Polymicrobial infection
- More common after c/s
- Prolonged ruptured membranes
- Chorioamnionitis
PP / Post-Op Fever
- Causes and symptoms
- Wind (atelectasis, pneumonia)
- Wound (seroma, necrotizing fasciitis)
- Water (UTI)
- Walk (thrmobophlebitis)
- Wonder drug (drug reaction)
- Womb (endometriosis)
- Wean (mastitis, engorgement)
