Organic Chemistry
From Ibstudy
(Difference between revisions)
PugnaciousG (Talk | contribs) (→Isomerism) |
PugnaciousG (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
====Alkenes==== | ====Alkenes==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *These structures are similar to the alkanes except two hydrogens are replaced by a double bond between two carbons | ||
| + | *The number '1' in the names refers to the position of the carbon starting the double bond. No numbering is needed in the first two members as there can be no ambiguity | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Ethene.gif]] Ethene | ||
| + | [[Image:Propene.gif]] Propene | ||
| + | [[Image:But-1-ene.gif]] But<nowiki>-</nowiki>1<nowiki>-</nowiki>ene | ||
| + | [[Image:Pent-1-ene.gif]]Pent<nowiki>-</nowiki>1<nowiki>-</nowiki>ene | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Combustion==== | ||
| + | *Complete combustion of a hydrocarbon produces CO2 and H2O | ||
| + | *Incomplete produces CO, C, and H2O | ||
| + | *Incomplete combustion is where the carbon is not completely oxidized | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==11.3 Other Functional Groups== | ||
{|border="1" cellpading="5" cellspacing="0" align="center" | {|border="1" cellpading="5" cellspacing="0" align="center" | ||
Revision as of 20:33, 5 January 2008
Contents |
11.1 Homologous series
- A homologous series is a set of compounds with one repeating functional group
Physical Properties of Alkanes
- As chain length increases, so does boiling point, as an increased number of electrons causes stronger Van de Waal forces
- The increase in boiling temperature is rapid at first, but flattens off
11.2 Hydrocarbons
- Compounds containing only Hydrogen and carbon
- Three examples,
- Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes
Alkanes
- Alkanes have a CH3 group at each end, and are made up of CH2 groups.
- First five are,
- Methane
- Ethane
- Propane
- Butane
- Pentane
 Methane
Methane
 Ethane
Ethane
 Propane
Propane
 Butane
etc.
Butane
etc.
Isomerism
- The idea that one hydrocarbon can exist in another form or structure. This will occur if:
- Each carbon forms four bonds
- Each hydrogen forms one bond
- Each oxygen forms two bonds
- If the bonds formed are not straight, the isomer is known to be branched
- Here is an example with C4H10
 Butane (C4H10)
Butane (C4H10)
 Methyl Propane (C4H10)
Methyl Propane (C4H10)
Alkenes
- These structures are similar to the alkanes except two hydrogens are replaced by a double bond between two carbons
- The number '1' in the names refers to the position of the carbon starting the double bond. No numbering is needed in the first two members as there can be no ambiguity
 Ethene
Ethene
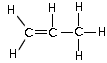 Propene
Propene
 But-1-ene
But-1-ene
 Pent-1-ene
Pent-1-ene
Combustion
- Complete combustion of a hydrocarbon produces CO2 and H2O
- Incomplete produces CO, C, and H2O
- Incomplete combustion is where the carbon is not completely oxidized
11.3 Other Functional Groups
| Functional Group Name | Functional Group |
| Aldehyde | -CHO |
| Ketone | -CO- |
| Alcohol | -OH |
| Carboxylic Acid | -COOH |
| Amine | -NH2 |
| Amide | -CONH2 |
| Halogenoalkane | -X (Any Halogen) |
| Ester | -COO- |
| Ether | -O- |
