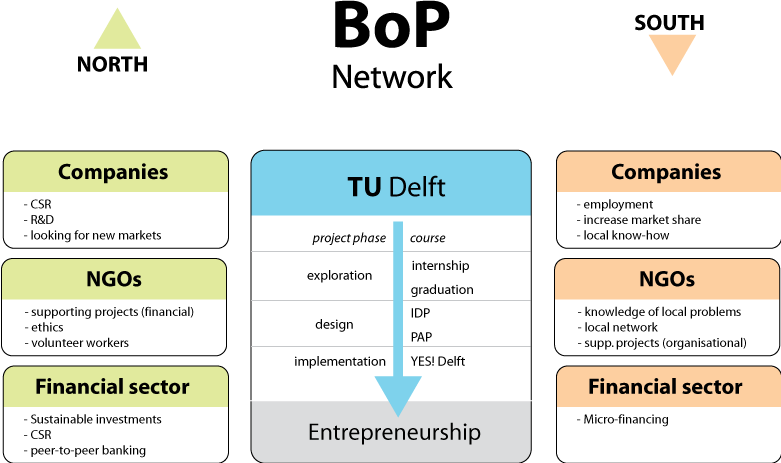
Network
From Bop
(→Goals) |
(→Goals) |
||
| Line 337: | Line 337: | ||
=====Goals===== | =====Goals===== | ||
The Inter-American Bank wishes to ”contribute to the acceleration of the process of economic and social development of the regional developing member countries, individually and collectively.” The Bank’s two main goals are to promote poverty reduction and social equity as well as environmentally sustainable growth. To attain these goals, the Bank focuses its work on four priority areas: | The Inter-American Bank wishes to ”contribute to the acceleration of the process of economic and social development of the regional developing member countries, individually and collectively.” The Bank’s two main goals are to promote poverty reduction and social equity as well as environmentally sustainable growth. To attain these goals, the Bank focuses its work on four priority areas: | ||
| + | |||
1. Fostering competitiveness through support for policies and programs that increase a country's potential for development in an open global economy. | 1. Fostering competitiveness through support for policies and programs that increase a country's potential for development in an open global economy. | ||
| + | |||
2. Modernizing the state by strengthening the efficiency and transparency of public institutions. | 2. Modernizing the state by strengthening the efficiency and transparency of public institutions. | ||
| + | |||
3. Investing in social programs, economic activities and infrastructure to expand opportunities for the poor and for the majority of the population. | 3. Investing in social programs, economic activities and infrastructure to expand opportunities for the poor and for the majority of the population. | ||
| + | |||
4. Promoting regional economic integration by forging links among countries to develop larger markets for their goods and services. | 4. Promoting regional economic integration by forging links among countries to develop larger markets for their goods and services. | ||
=====Strengths & Expertise===== | =====Strengths & Expertise===== | ||
=====Example projects===== | =====Example projects===== | ||
Revision as of 23:10, 12 May 2008
goal
features
first model
Stakeholders
TU Delft
courses of relevance: Internationalization (ID4050)
Bachelor
Minor International entrepreneurship and development
- Social Entrepreneurship (WM0565TU, Esther Blom)
- Awareness of Cultural Differences (SPM9237, Martin de Jong)
- Technology and Global Development (WM0902TU, Wim Ravensteijn)
- Collaborative Business Design (IO3813, Frido Smulders)
- History of Technology (WM0401TU, Wim Ravensteijn)
- Casestudy International Entrepreneurship & Development (WM0564TU, Esther Blom )
Electives
- History of Technology & Technology and Global Development (WM0930TU, Wim Ravensteijn)
- Communicative interaction: Moral aspects of teamwork (WM0306TU, Otto Kroesen)
- Intercultural internship (WM0927TU, Otto Kroesen)
- De onderneming in sociologisch perspectief (WM0404TU)
- Duurzaam ondernemen (WM0915TN)
- Product Development en Innovatie(IO3803)
- Communicative Interaction (WM0306TU)
- Innovatiemanagement (WM0625TU)
- Civiele Techniek in ontwikkelingssamenwerking (CT5560)
- De essentie van technologisch Ondernemersschap (WM0560TU)
- Finance for Entrepreneurs (WB3482)
- Managing Start-ups (WM0926TU)
- Introduction to business marketing (IO3806)
Master
IDP / PAP / Graduation Project / Internship
- Internationalisation (ID4250)
Students
TU Delft Sustainability related organisations
CICAT
Cicat is a organization which manages internships and graduations projects out side of western Europe. They’re nit interested in the content of the projects. They are just sereaching to match a student to a company and arrange everything. They work for the whole TU Delft, but see them selves as a small part inside the TU Delft network. Most project come from inside the faculties themselves, through the internship coordinator of the faculties. For BOP projects most contact go by the professors of the faculties. CICAT provides 300 euros per BoP project.
S4S
Their main goal is further developing exciting project, from a BoP internship or graduation project. Developing already exciting product in to companies, the build of the product and putting them on the market. Their second goal is to persuade and make everybody inside the TU Delft enthusiastic to use their knowledge and abilities to help people in developing countries. Currently they have three projects Ice-cream cars Ghana Moves EcoHotel Cassave machine S4S only excists 1 year. It consists of 5 students who work on this approximately 1 day a week. Eventhough it is a young organization they see the use of S4S in the future. They really see the use of a network that connects all the organizations connected to the TU Delft that are working in connection to BoP projects. There are often companies that contact them because they have a project and want the S4S involved in really doing the project. Currently Africa is included in the logo but they are also open to other parts of the world. They cannot wait to expand.
International Research Delft
An organization for innovative research for companies in development. This year they will go to India. These projects are not BoP.
SierraLeone
Is a project with a group of students from the whole TU Delft. They work together with a Dutch company called Yacht. Currently they build a hospital in SierraLeone. No one from here is currently there the build is done by the people them selves. One of the people involved is a IDE student.
Osiris
They don’t organize projects. They share knowledge about sustainable topics: solar panels, biogas ect. They are working independently. They organize excursions, have their own magazine and a large website.
Platform DO (TBM)
The platform consists of professors and students connected to the TBM faculty. In every meeting they take 3 students with them, one from Osisris, one from ORAS and one from AAG. They are working on sustainability projects.
Engineers without borders
Is very busy on BoP projects.
Cooperation between the organizations
S4S and Osiris work together very well. Some students are involved in both organizations. SierraLeone is less in contact with these two. Most other organization do not really cooperate and know little of each other. Most students who have conducted a BoP project have struggle to find the right contact. At this moment there are a lot of organizations related to the BoP. Student currently have to start contacting all of them themselves. Everybody is doing the same thing over and over again.
Interesting to be present at
In the week of the 19th of May there is a meeting between S4S and Osiris, organized by Lisanne, from TBM.
Contacts
Esther Blom (Delft entrepreneurship main contact) www.dce.tudelft.nl
S4S Danielle 06-42070077 Martijn 06-42750520
Civil Engineering Henk-Jan Verhagen (main contact)
TBM- Platform DO (Is working on sustainability projects) Gert-Jan de Werk g.dewerk@tudelft.nl
IDE J.C. Dielh Probu Kandachar (main BoP contact)
Survey among students interested in BoP
What is your biggest motivation do to a bop project?
Why do you want to go to a specific country?
How went the process of searching for the project?
How went the process of the project it self?
Did you miss some support?
What would you have liked to know more before you went?
Would you have a preference to find group members yourself, people you already know?
Is it important that the project you will be doing is a BoP project? What was your main motivation? Consciously BoP or not?
How important is the difference in culture for you?
Was it hard to find a project?
Do you have good contact with TU delft?
NGOs
First of all is important define the concept of non-governmental organization (NGO), we are using two different definitions. The first concept following the United Nations Organization (UN) definition and the other address the general concept.
According to the United Nations Organization, a Non Governmental Organization is: “is a not-for-profit, voluntary citizens’ group, which is organized on a local, national or international level to address issues in support of the public good. Task-oriented and made up of people with common interests, NGOs perform a variety of services and humanitarian functions, bring citizens’ concerns to governments, monitor policy and programme implementation, and encourage participation of civil society stakeholders at the community level. They provide analysis and expertise, serve as early warning mechanisms, and help monitor and implement international agreements. Some are organized around specific issues, such as human rights, the environment or health. Their relationship with offices and agencies of the United Nations (UN) system differs depending on their location and their mandate.” http://www.un.org/dpi/ngosection/criteria.asp
And Following Wikipedia, NGO is: “a legally constituted organization created by private persons or organizations with no participation or representation of any government. In the cases in which NGOs are funded totally or partially by governments, the NGO maintains its non-governmental status insofar as it excludes government representatives from membership in the organization.” http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NGO
Cordaid
Relation Management
Wanted: a partner for a long-standing relationship, with this appeal, the Relation Management Department started a number of activities to strengthen the co-operation with Dutch educational institutions, capital funds, foundations, companies, service clubs and financial institutions. This co-operation is important, because poverty and injustice can only be fought with joint efforts. Especially innovative types of co-operation are sought, while the use of expertise and influence are at least as important as income acquisition. The last mentioned is obviously not unimportant either, as a result of which the fund-raising efforts of the Relation Management Department in 2006 have resulted in proceeds of 6.6 million due to contributions from companies, capital funds, educational institutions, ecclesiastical institutions and service clubs.
source: Cordaid Annual report 2006 (download here)
Avina
Ashoko
Bid-network
Companies
Consultancies
Governmental Organisations
NCDO
Financial Sector
peer-to-peer banking
Triodos Bank
The Triodos Bank fynances compagnies, institutions and project with an added value in the field of social, enviroment and cultural. For this the bank uses money from savers and investors who chose to invest in a social and durable concern.
Mission • Being part of a society in which the living standart is raised and human value is the main focus. • They want to provide people , companies and organisations to make conscious use of their money and promote durable developments • Giving their clients a durable financial product and good service.
Fair Share Fund A private investment option, which invests in local entrepreneurs in developing countries. Fair Share Fund helps people in Central-Asia and Eastern-Europe to start their own business or expand their business.
http://www.triodos.nl/nl/personal_banking/investments/investment_types/43502/
Terrafina Microfinance
A micro fynancing program of the ICCO, Oikocredit and Rabobank Foundation. They are active worldwide. They don’t provide micro credits themselves. They support young local credit organisations in their starting phase with allowances and advise. More experienced organisations get loans to expand their activities. These organisations do provide micro credits. Terrafina Microfinance only operates in Africa.
http://www.terrafina.nl/en/index.phtml?p=Vraag+en+antwoord
AMSA
Argentina Microfinanzas S.A. (AMSA) is a start-up microfinance institution set up by an experienced management team with good loans methodology and a solid business plan.
http://www.triodos.com/com/who_we_finance/funds/triodos_doen_foundation/latin_america/207900
The foundation Triodos-Doen
Is a coorporation between the Triodos Bank and the DOEN foundation. Their goal is to stimulate project which concern durable developments in developing countries. The foundation Triodos-Doen focusses on MFI’s and fair trade organisations and biological products with a fair trade label.
http://www.doen.nl/web/show/id=44589
FIS
FIS is the second largest MFI in Argentina. In addition to loans, it provides solar panels to families living in zones where there is no commercial electricity.
http://www.socialedge.org/blogs/global-x/topics/Argentina
RADIM Red Argentina de instituciones de Microcrédito
Aims • To give support and to strengthen the professionalization of Human resources of the IMF partners. • To generate compromised Human Resources to institutions, to offer services of high quality to the people for those who work for.
Services • To achieve the mentioned aims it is planed to implement different actions and intervention methodologies: • Thematic trainings integrating several IMF (Seminars, Workshops, courses, etc.) • Specializing trainings at field in every IMF (from demand) • Internship Programme between the IMF. • Services of technical assistance to the IMF. • Training actions at distance (Internet and systems of videoconference) • Events of training on microfinance, national and international.
http://www.reddemicrocredito.org/eng/servicios.asp
Kiva
Mission: connecting people through lending for the sake of alleviating poverty
Kiva empowers individuals to lend directly to entrepreneurs in the developing world. They work together with existing expert microfinance institutions.
International Aid Organizations
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an international organization whose stated aims are to facilitate cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress and human rights issues. The UN was founded in 1945 to replace the League of Nations, to stop wars between nations and to provide a platform for dialogue.
Goals
The Millennium Development Goals are eight goals that all 192 United Nations member states have agreed to try to achieve by the year 2015.[30] The United Nations Millennium Declaration, signed in September 2000, commits the states to: 1. eradicate extreme poverty and hunger; 2. achieve universal primary education; 3. promote gender equality and empower women; 4. reduce child mortality; 5. improve maternal health; 6. combat HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases; 7. ensure environmental sustainability; and 8. develop a global partnership for development.
Strengths & Expertise
Example projects
World Bank
The World Bank is a collection of international organizations to aid countries in their process of economic development with loans, advice, and research. It was founded in the 1940s to aid Western European countries after World War II with capital.
Goals
The World Bank, makes loans to developing countries for development programmes with the stated goal of reducing poverty
Strengths & Expertise
It includes four agencies: the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD or 'World Bank') which provides hard loans to countries for projects (with relatively high interest rates and shorter repayment periods); the International Development Association (IDA) which provides soft loans or grants to countries (with low or no interest and long repayment periods); the International Finance Corporation (IFC) which is the private sector arm of the World Bank and encourages private business and investment in developing countries; and, the Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA) which guarantees funds that private investors direct to developing countries.
Example projects in Argentina
The key features of the World Bank program in Argentina include the following projects:
•Plan Nacer – The loan for US$300 million guarantees health services to mothers and children in the northeast and northwest regions, where the country’s nine poorest provinces are located.
• Proinder - supports improving the productive and organizational capacity of poor rural communities and strengthening national and provincial rural development policy. The Bank supported Proinder with a US$75 million investment loan and granted an extension in 2007 of US$45 million to allow the program to expand and reach 72,000 households from the 30,000 originally contemplated.
• Heads of Household Transition – the US$350 million project helps fund the implementation of a transition strategy to improve employment prospects and job placement for current participants in the Heads of Household program. The Heads of Household is an emergency “safety-net” program created by the Government of Argentina in 2002 that provides income support to unemployed head of households.
• Rural Education Improvement Project (PROMER) - the US$150 million loan supports the national government policy for rural education.
Analytical Agenda: The Bank is providing an extended plan of analytical work to Argentina including, among others, a poverty assessment focused on the links between informality, poverty, and inequality and a social protection study to support the transition from the Heads of Household program to a more permanent social safety net.
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is an agency of the United Nations founded in 1948. It is responsible for providing leadership on global health matters, shaping the health research agenda, setting norms and standards, articulating evidence-based policy options, providing technical support to countries and monitoring and assessing health trends.
Goals
The WHO aims to promote technical cooperation for health among nations, carry out programs to control and eradicate disease, and strive to improve the quality of human life. To reach its goals, the WHO has adopted the following agenda- 1. Promoting development 2. Fostering health security 3. Strengthening health systems 4. Harnessing research, information and evidence 5. Enhancing partnerships 6. Improving performance
Strengths & Expertise
Te World Bank has solid expertise on economic management and how to foster poverty-reducing growth through education, agriculture, bank supervision, major infrastructure, small business development, or pension and judicial reform - which is based on practical experience around the world. Another strength is that the WOrld Bank is capable of providing global public goods. With its financial heft and technical expertise, the bank is more capable of addressing issues that are beyond the scope of any single nation state.
Example projects
A pilot project to train doctors in diagnosing and treating epilepsy will assess the number of people suffering from epilepsy in the participating provinces and train primary health care workers within the existing primary health service how best to diagnose and treat epilepsy patients. In developing countries, there are issues such as social stigma and discrimination, lack of trained personnel and shortages of anti-epileptic drugs.
The Inter-American Development Bank
The Inter-American Development Bank (IDB, or IADB), was established and headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States, in 1959 to support Latin American and Caribbean economic and social development and regional integration by lending mainly to governments and government agencies, including State corporations. The IDB makes loans to the governments of its borrowing member countries at standard commercial rates of interest, and has preferred creditor status, meaning that borrowers will repay loans to the IDB before repaying other obligations to other lenders such as commercial banks. Argentina is a borrowing member country.
Goals
The Inter-American Bank wishes to ”contribute to the acceleration of the process of economic and social development of the regional developing member countries, individually and collectively.” The Bank’s two main goals are to promote poverty reduction and social equity as well as environmentally sustainable growth. To attain these goals, the Bank focuses its work on four priority areas:
1. Fostering competitiveness through support for policies and programs that increase a country's potential for development in an open global economy.
2. Modernizing the state by strengthening the efficiency and transparency of public institutions.
3. Investing in social programs, economic activities and infrastructure to expand opportunities for the poor and for the majority of the population.
4. Promoting regional economic integration by forging links among countries to develop larger markets for their goods and services.