Libya
From Roach Busters
(→Geography) |
|||
| Line 206: | Line 206: | ||
Libya extends over 1,759,540 square kilometres (679,182 sq. mi). It is somewhat smaller than Indonesia, and roughly the size of the US state of Alaska. It is bound to the north by the Mediterranean Sea, the west by Tunisia and Algeria, the southwest by Niger, the south by Chad and Sudan and to the east by Egypt. At 1770 kilometres (1100 miles), Libya's coastline is the longest of any African country bordering the Mediterranean. The portion of the Mediterranean Sea north of Libya is often called the Libyan Sea. The climate is mostly dry and desert-like in nature. However, the northern regions enjoy a milder Mediterranean climate. | Libya extends over 1,759,540 square kilometres (679,182 sq. mi). It is somewhat smaller than Indonesia, and roughly the size of the US state of Alaska. It is bound to the north by the Mediterranean Sea, the west by Tunisia and Algeria, the southwest by Niger, the south by Chad and Sudan and to the east by Egypt. At 1770 kilometres (1100 miles), Libya's coastline is the longest of any African country bordering the Mediterranean. The portion of the Mediterranean Sea north of Libya is often called the Libyan Sea. The climate is mostly dry and desert-like in nature. However, the northern regions enjoy a milder Mediterranean climate. | ||
| - | Natural hazards come in the form of hot, dry, dust-laden sirocco (known in Libya as the gibli). This is a southern wind blowing from one to four days in spring and autumn. There are also dust storms and sandstorms. Oases can also be found scattered throughout Libya, the most important of which are Ghadames and Kufra as well as others. | + | Natural hazards come in the form of hot, dry, dust-laden sirocco (known in Libya as the ''gibli''). This is a southern wind blowing from one to four days in spring and autumn. There are also dust storms and sandstorms. Oases can also be found scattered throughout Libya, the most important of which are Ghadames and Kufra as well as others. |
===Libyan Desert=== | ===Libyan Desert=== | ||
Revision as of 10:22, 5 March 2008
| جمهورية ليبيا الشعبية Al-Jamāhīriyyah al-Lībiyyah aš-Ša`biyyah People's Republic of Libya | |
| | |
 | 
|
| Flag | Coat of arms |
| | |
| Motto "al-Watan, at-Thawra, al-Wehda" (Arabic) "Nation, Revolution, Unity" | |
| | |
| Anthem The Internationale | |
| | |

| |
| | |
| Capital (and largest city) | Tripoli 32°54′N, 13°11′E |
| | |
| Official languages | Arabic |
| | |
| Demonym | Libyan |
| | |
| Government - General-Secretary - Premier - Politburo President | Socialist state Muammar al-Gaddafi Baghdadi Mahmudi Miftah Muhammed K'eba |
| | |
| Establishment - Relinquished by Italy - Independence - Coup d'état | February 10, 1947 December 24, 1951 September 1, 1969 |
| | |
| Area - Total - Water (%) | 1,759,540 km² 679,359 sq mi negligible |
| | |
| Population - July 2007 estimate - 2006 census - Density | 6,036,914 5,670,688 3.2 /km² 8.4 /sq mi |
| | |
| GDP (PPP) - Total - Per capita | 2007 estimate $59.31 billion $9,825 |
| | |
| GDP (nominal) - Total - Per capita | 2007 estimate $55.83 billion $9,248 |
| | |
| Gini (2000) | 25 (low) |
| | |
| HDI (2005) | |
| | |
| Currency | Dinar (LYD)
|
| | |
| Time zone - Summer (DST) | EET (UTC +2) not observed (UTC +2) |
| | |
| Internet TLD | .ly |
| | |
| Calling code | +218 |
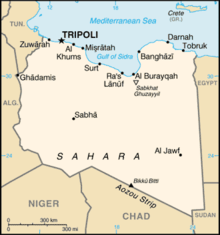
Libya (Arabic: ليبيا Lībiyā; Libyan vernacular: Lībya), officially the People's Republic of Libya (Arabic: جمهورية ليبيا الشعبية Al-Jamāhīriyyah al-Lībiyyah aš-Ša`biyyah), is a country in North Africa. Bordering the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Libya lies between Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west. With an area of almost 1.8 million square kilometres (700,000 sq mi), 90% of which is desert, Libya is the fourth largest country in Africa by area. The capital, Tripoli, is home to 1.7 million of Libya's 6 million people. The three traditional parts of the country are Tripolitania, the Fezzan and Cyrenaica.
The name "Libya" is a indigenous (i.e. Berber) one, which is attested in ancient Egyptian texts as ![]() , R'bw (= Libu), which refers to one the tribes of Berber peoples living west of the Nile. In Greek the tribesmen was called Libyes and their country became "Libya", although in ancient Greece the term had a broader meaning, encompassing all of North Africa west of Egypt. Later on, at the time of Ibn Khaldun, the same big tribe was known as Lawata.
, R'bw (= Libu), which refers to one the tribes of Berber peoples living west of the Nile. In Greek the tribesmen was called Libyes and their country became "Libya", although in ancient Greece the term had a broader meaning, encompassing all of North Africa west of Egypt. Later on, at the time of Ibn Khaldun, the same big tribe was known as Lawata.
Libya's GDP (PPP) is one of the continent's highest; this is largely due to its large petroleum reserves and low population.
Libya has been ruled as a Marxist-Leninist state since 1969, when Colonel Muammar al-Gaddafi deposed the pro-Western King Idris I in a bloodless coup. Libya has since become one of the Soviet Union's most consistent and loyal allies, while being viewed by much of the Western world with deep suspicion, due in part to Gaddafi's open support of "national liberation movements" around the world.
Contents |
History
Archaeological evidence indicates that from as early as the 8th millennium BC, Libya's coastal plain was inhabited by a Neolithic people who were skilled in the domestication of cattle and the cultivation of crops. The area known in modern times as Libya was later occupied by a series of peoples, with the Phoenicians, Carthaginians, Greeks, Romans, Vandals and Byzantines ruling all or part of the area. Although the Greeks and Romans left ruins at Cyrene, Leptis Magna and Sabratha, little other evidence remains of these ancient cultures.
Phoenicians
The Phoenicians were the first to establish trading posts in Libya, when the merchants of Tyre (in present-day Lebanon) developed commercial relations with the Berber tribes and made treaties with them to ensure their cooperation in the exploitation of raw materials. By the 5th century BC, Carthage, the greatest of the Phoenician colonies, had extended its hegemony across much of N.Africa, where a distinctive civilisation, known as Punic, came into being. Punic settlements on the Libyan coast included Oea (Tripoli), Libdah (Leptis Magna) and Sabratha. All these were in an area that was later called Tripolis, or "Three Cities". Libya's current-day capital Tripoli takes its name from this.
Greeks
The Greeks conquered Eastern Libya when, according to tradition, emigrants from the crowded island of Thera were commanded by the oracle at Delphi to seek a new home in North Africa. In 630 BC, they founded the city of Cyrene. Within 200 years, four more important Greek cities were established in the area: Barce (Al Marj); Euhesperides (later Berenice, present-day Benghazi); Teuchira (later Arsinoe, present-day Tukrah); and Apollonia (Susah), the port of Cyrene. Together with Cyrene, they were known as the Pentapolis (Five Cities).
Romans
The Romans unified all three regions of Libya, and for more than 600 years Tripolitania and Cyrenaica became prosperous Roman provinces. Roman ruins, such as those of Leptis Magna, attest to the vitality of the region, where populous cities and even small towns enjoyed the amenities of urban life. Merchants and artisans from many parts of the Roman world established themselves in North Africa, but the character of the cities of Tripolitania remained decidedly Punic and, in Cyrenaica, Greek.
Arabs
Arabs under General Abdullah ibn Saad conquered Libya in the 7th century AD during the reign of Caliph Usman. In the following centuries, many of the indigenous peoples adopted Islam, and also the Arabic language and culture.
Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turkey conquered the country in the mid-16th century, and the three States or "Wilayat" of Tripolitania, Cyrenaica and Fezzan (which make up Libya) remained part of their empire with the exception of the virtual autonomy of the Karamanlis. The Karamanlis ruled from 1711 until 1835 mainly in Tripolitania, but had influence in Cyrenaica and Fezzan as well by the mid 18th century. This constituted a first glimpse in recent history of the united and independent Libya that was to re-emerge two centuries later. Ironically, reunification came about through the unlikely route of an invasion (Italo-Turkish War, 1911-1912) and occupation starting from 1911 when Italy simultaneously turned the three regions into colonies.
Italian colony
From 1912 to 1927, the territory of Libya was known as Italian North Africa. From 1927 to 1934, the territory was split into two colonies, Italian Cyrenaica and Italian Tripolitania run by Italian governors.
In 1934, Italy adopted the name "Libya" (used by the Greeks for all of North Africa, except Egypt) as the official name of the colony (made up of the three Provinces of Cyrenaica, Tripolitania and Fezzan). King Idris I, Emir of Cyrenaica, led Libyan resistance to Italian occupation between the two World Wars. From 1943 to 1951, Tripolitania and Cyrenaica were under British administration, while the French controlled Fezzan. In 1944, Idris returned from exile in Cairo but declined to resume permanent residence in Cyrenaica until the removal of some aspects of foreign control in 1947. Under the terms of the 1947 peace treaty with the Allies, Italy relinquished all claims to Libya.
United Kingdom of Libya
On November 21, 1949, the UN General Assembly passed a resolution stating that Libya should become independent before January 1, 1952. Idris represented Libya in the subsequent UN negotiations. On December 24, 1951, Libya declared its independence as the United Kingdom of Libya, a constitutional and hereditary monarchy under King Idris.
The discovery of significant oil reserves in 1959 and the subsequent income from petroleum sales enabled one of the world's poorest nations to establish an extremely wealthy state. Although oil drastically improved the Libyan government's finances, popular resentment began to build over the increased concentration of the nation's wealth in the hands of King Idris and the national elite. This discontent continued to mount with the rise of Nasserism and Arab nationalism throughout North Africa and the Middle East.
Coup of Muammar al-Gaddafi
to be added
Politics
Libya has been governed as a single-party socialist republic since September 1, 1969, when Colonel Muammar al-Gaddafi deposed the monarchy in a bloodless coup. Since then, Gaddafi has implemented far-reaching and monumental changes, both good and bad. While life expectancy, literacy, health care, and women's rights have improved dramatically, Gaddafi's iron grip on the country remains as firm as ever, and all vestiges of dissent - real or imaginary - are ruthlessly suppressed.
As General-Secretary of the Libyan Workers' Party, Gaddafi is the de facto leader of Libya. In theory, Baghdadi Mahmudi is the head of state and head of government. He simultaneously holds the positions of Premier, Chairman of the Council of People's Commissars, and Chairman of the Council of Ministers, and (on paper at least) holds vast powers; in reality, his position is a largely ceremonial one, and he is in effect a powerless figurehead totally beholden to Gaddafi.
While the constitution stipulates that the Political Bureau (Politburo) of the Libyan Workers' Party elects the General-Secretary, such an election has never taken place, nor will Colonel Gaddafi permit such an election so long as he remains at the helm.
In theory, supreme power in the party is invested in the Party Congress. However, in practice supreme power is the domain of the General-Secretary. At lower levels, the organizational hierarchy is managed by Party Committees headed by elected party committee secretaries. The bottom level of the Party is the primary party organization or party cell; the management of a cell is called party bureau. A party bureau is headed by the elected bureau secretary. At smaller party cells, secretaries are regular employees of the corresponding plant/hospital/school/etc. Sufficiently large party organizations are usually headed by an exempt secretary, who draws his salary from the Party money.
In spite of Gaddafi's egalitarian rhetoric, a small sector of the population has, through membership in the ruling party, become a new elite class. High-ranking party members enjoy many perquisites denied to the average Libyan citizen, such as shopping at well-stocked stores, access to foreign merchandise, preference in obtaining housing, access to holiday resorts, being allowed to travel abroad, send their children to the best universities, and obtain prestigious jobs (as well as party membership itself) for their children. This has spawned a patronage system fraught with corruption.
The national legislature of Libya is the unicameral, 2700-member General People's Congress, whose members are directly elected by popular vote through a system of proportional representation. While oftentimes many candidates will vie for a single constituency, only those who meet rigorous guidelines and are known to "support the revolution" are allowed to hold office, ensuring that the candidates differ little from each other, if at all. Many candidates are hand-picked by the Politburo and other powerful figures in the government. Due to the absence of viable alternatives, voter apathy is rife; this is belied, however, by the extremely high voter turnout at elections (voting is compulsory, and those who do not register to vote face a heavy fine, imprisonment, or worse). According to human rights organizations and Libyan exiles, the General People's Congress is essentially a "rubber stamp" legislature that holds no power. In fact, real legislative power is wielded by the Central Committee of the Libyan Workers' Party, while the General People's Congress is relegated to the subordinate position of approving party initiatives. The constitution provides for only limited legislative powers, in that members of the General People's Congress, elected to five-year terms, have the right to initiate laws "concurrently" with the General-Secretary.
The Libyan court system consists of four levels: summary courts, which try petty offenses, the courts of first instance, which try more serious crimes; the courts of appeals, and the Supreme Court, which is the final appellate level. The General People's Congress appoints justices to the Supreme Court. The judiciary is not independent, and those justices who do not toe faithfully toe the party line are forcibly "retired," and replaced with more compliant individuals.
On paper, Libya is a highly-decentralized, directly democratic "state of the masses," but this is illusory. Libya is actually a centralized, unitary state, and Local People's Congresses, while directly and popularly elected, are totally subordinate to the national government. Even the tiniest gesture of autonomy from Tripoli is not tolerated. Just as with national elections, voting in local elections is compulsory and enforced.
On a positive note, women and minorities hold a sizeable portion of seats in both local and national government, and their growing political clout has mirrored the general shrink in disparity between women and men - almost unheard of in a predominantly Muslim country.
Libya has been fully secular since Gaddafi's ascent to power, and Gaddafi has skillfully played upon foreign and domestic fears of Islamist extremism to his advantage by labelling his opponents as "extremists" as a pretext for quashing them.
Foreign relations
to be added
Human rights
to be added
Libya is unusual among communist states in that it generally respects religious freedom, and the small Christian and Jewish minorities enjoy relatively cordial relations with the Muslim majority.
Subdivisions
| Libya is divided into 32 sha'biyah, which are listed as follows: | ||
| 1 Ajdabiya | 17 Ghat | |
| 2 Al Butnan | 18 Ghadamis | |
| 3 Al Hizam Al Akhdar | 19 Gharyan | |
| 4 Al Jabal al Akhdar | 20 Murzuq | |
| 5 Al Jfara | 21 Mizdah | |
| 6 Al Jufrah | 22 Misratah | |
| 7 Al Kufrah | 23 Nalut | |
| 8 Al Marj | 24 Tajura Wa Al Nawahi AlArba' | |
| 9 Al Murgub | 25 Tarhuna Wa Msalata | |
| 10 An Nuqat al Khams | 26 Tarabulus (Tripoli) | |
| 11 Al Qubah | 27 Sabha | |
| 12 Al Wahat | 28 Surt | |
| 13 Az Zawiyah | 29 Sabratha Wa Surman | |
| 14 Benghazi | 30 Wadi Al Hayaa | |
| 15 Bani Walid | 31 Wadi Al Shatii | |
| 16 Darnah | 32 Yafran | |
Geography
Libya extends over 1,759,540 square kilometres (679,182 sq. mi). It is somewhat smaller than Indonesia, and roughly the size of the US state of Alaska. It is bound to the north by the Mediterranean Sea, the west by Tunisia and Algeria, the southwest by Niger, the south by Chad and Sudan and to the east by Egypt. At 1770 kilometres (1100 miles), Libya's coastline is the longest of any African country bordering the Mediterranean. The portion of the Mediterranean Sea north of Libya is often called the Libyan Sea. The climate is mostly dry and desert-like in nature. However, the northern regions enjoy a milder Mediterranean climate.
Natural hazards come in the form of hot, dry, dust-laden sirocco (known in Libya as the gibli). This is a southern wind blowing from one to four days in spring and autumn. There are also dust storms and sandstorms. Oases can also be found scattered throughout Libya, the most important of which are Ghadames and Kufra as well as others.
Libyan Desert
The Libyan Desert, which covers much of eastern Libya, is one of the most arid places on earth. In places, decades may pass without rain, and even in the highlands rainfall happens erratically, once every 5–10 years. At Uweinat, the last recorded rainfall was in September 1998. There is a large depression, the Qattara Depression, just to the south of the northernmost scarp, with Siwa oasis at its western extremity. The depression continues in a shallower form west, to the oases of Jaghbub and Jalo.
Likewise, the temperature in the Libyan desert can be extreme; in 1922, the town of Al 'Aziziyah, which is located west of Tripoli, recorded an air temperature of 57.8 °C (136.0 °F), generally accepted as the highest recorded naturally occurring air temperature reached on Earth.
There are a few scattered uninhabited small oases, usually linked to the major depressions, where water can be found by digging to a few feet in depth. In the west there is a widely dispersed group of oases in unconnected shallow depressions, the Kufra group, consisting of Tazerbo, Rebianae and Kufra. Aside from the scarps, the general flatness is only interrupted by a series of plateaus and massifs near the centre of the Libyan Desert, around the convergence of the Egyptian-Sudanese-Libyan Borders.
Slightly further to the south are the massifs of Arkenu, Uweinat and Kissu. These granite mountains are very ancient, having formed much before the sandstones surrounding them. Arkenu and Western Uweinat are ring complexes very similar to those in the Air Mountains. Eastern Uweinat (the highest point in the Libyan Desert) is a raised sandstone plateau adjacent to the granite part further west. The plain to the north of Uweinat is dotted with eroded volcanic features.
With the discovery of oil in the 1950s also came the discovery of a massive aquifer underneath much of the country. The water in this aquifer pre-dates the last ice ages and the Sahara desert itself. The country is also home to the Arkenu craters, double impact craters found in the desert.
Economy
to be added